| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
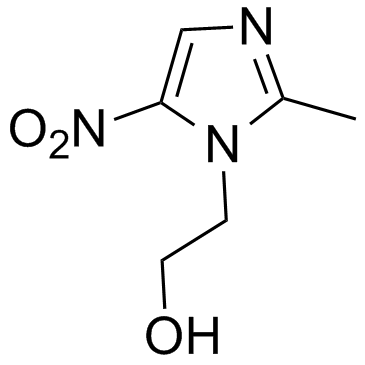 |
甲硝唑
CAS:443-48-1 |
|
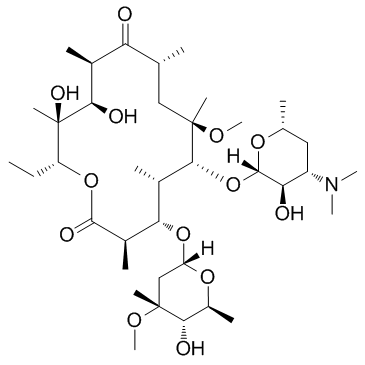 |
克拉霉素
CAS:81103-11-9 |
|
 |
利福昔明
CAS:80621-81-4 |
|
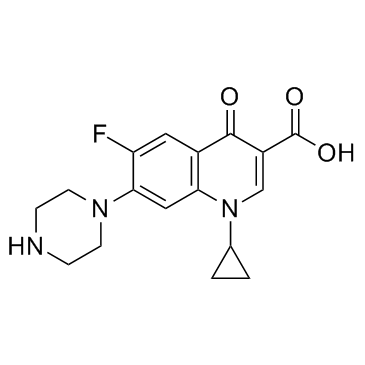 |
环丙沙星
CAS:85721-33-1 |
|
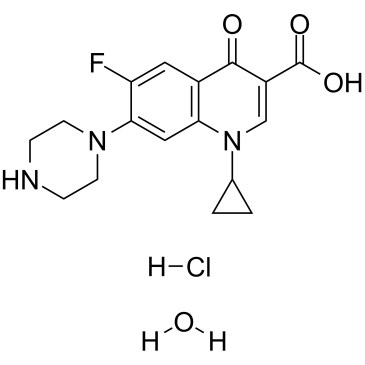 |
盐酸环丙沙星
CAS:86393-32-0 |