| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
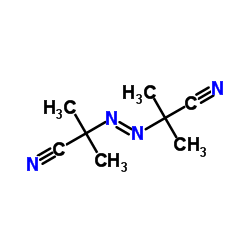 |
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
CAS:78-67-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
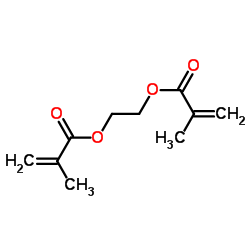 |
Ethylene methacrylate
CAS:97-90-5 |
|
 |
NAD+
CAS:53-84-9 |
|
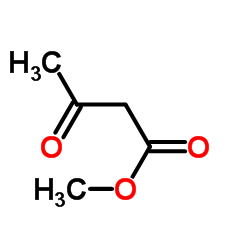 |
Methyl acetoacetate
CAS:105-45-3 |
|
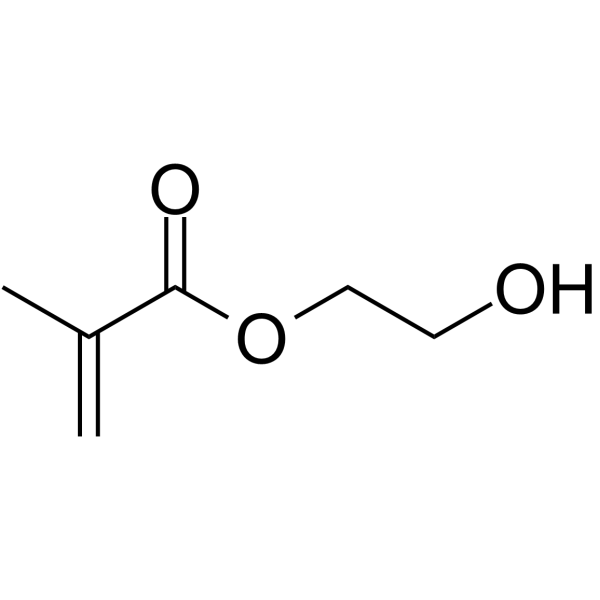 |
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate
CAS:868-77-9 |
|
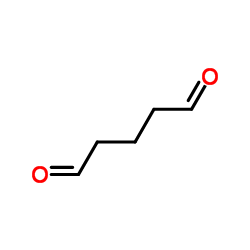 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |