Maltodextrin
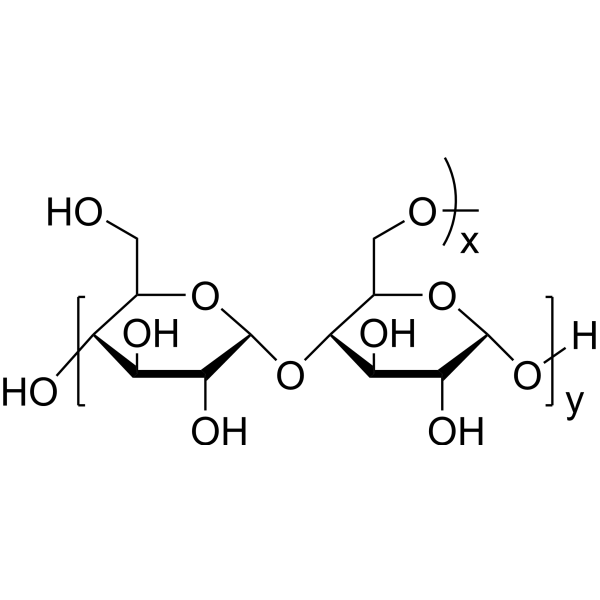
Maltodextrin structure
|
Common Name | Maltodextrin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9050-36-6 | Molecular Weight | 180.156 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 527.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | (C6H10O5)n·xH2O | Melting Point | 240ºC (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 286.7±26.6 °C | |
|
Identification and characterization of MalA in the maltose/maltodextrin operon of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius DSM639.
J. Bacteriol. 195(8) , 1789-99, (2013) A putative maltose/maltodextrin operon was found in the Sulfolobus acidocaldarius DSM639 genome. The gene cluster consisted of 7 genes (malA, trmB, amyA, malG, malF, malE, and malK). Here, we report the identification of MalA, which is responsible for the hyd... |
|
|
Vesicular powder as carrier for doxycycline hydrochloride and metronidazole combination therapy.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 19(6) , 755-68, (2014) In this study, vesicular proniosomal powder encapsulating doxycycline hydrochloride (DH) and metronidazole (MT) combination therapy was developed using different types of spans, cholesterol (CH) and maltodextrin as a carrier. Proniosomal powder was free flowi... |
|
|
Supramolecular complexes of maltodextrin and furosemide polymorphs: a new approach for delivery systems.
Carbohydr. Polym. 94(1) , 292-300, (2013) We present new supramolecular complexes of two different solid forms of furosemide (I or II) with maltodextrin, in order to explore their application as delivery systems improving the bioavailability of the drug. The complexation in solution was evaluated by ... |
|
|
Synthesis, characterization and toxicological evaluation of maltodextrin capped cadmium sulfide nanoparticles in human cell lines and chicken embryos.
J. Nanobiotechnology 10 , 47, (2012) Semiconductor Quantum dots (QDs) have become quite popular thanks to their properties and wide use in biological and biomedical studies. However, these same properties entail new challenges in understanding, predicting, and managing potential adverse health e... |
|
|
Prickly pear cactus (Opuntia ficus indica var. saboten) protects against stress-induced acute gastric lesions in rats.
J. Med. Food 15(11) , 968-73, (2012) The protective activity of prickly pear cactus (Opuntia ficus indica var. saboten) fruit juice and its main constituent, betanin, were evaluated against stress-induced acute gastric lesions in rats. After 6 h of water immersion restraint stress (WIRS), gastri... |
|
|
Effect of additives on freeze-drying and storage of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase.
Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 168(5) , 1101-7, (2012) The extracellular lipase of Yarrowia lipolytica presents numerous potentialities for biotechnological applications. This work describes the development and storage of powders obtained from supernatants containing Y. lipolytica lipase by freeze-drying as downs... |
|
|
Novel delivery approach for ketotifen fumarate: dissofilms formulation using 3² experimental design: in vitro/in vivo evaluation.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 19(5) , 521-30, (2014) Orally dissolving films (dissofilms) have gained increasing popularity and attention due to their ease of administration and avoidance of first pass metabolism. Ketotifen fumarate (KF) bioavailability is reported to be only ~ 50% due to hepatic first-pass met... |
|
|
Mechanism of maltodextrin transport through LamB.
Res. Microbiol. 153(7) , 417-24, (2002) The Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane contains several independent, biochemically distinct transport systems for the acquisition of solutes from the environment. Three or more different classes of membrane proteins exist within the porin superfamily, tha... |
|
|
Maltose uptake by the novel ABC transport system MusEFGK2I causes increased expression of ptsG in Corynebacterium glutamicum.
J. Bacteriol. 195(11) , 2573-84, (2013) The Gram-positive Corynebacterium glutamicum efficiently metabolizes maltose by a pathway involving maltodextrin and glucose formation by 4-α-glucanotransferase, glucose phosphorylation by glucose kinases, and maltodextrin degradation via maltodextrin phospho... |
|
|
Liver and muscle glycogen repletion using 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy following ingestion of maltodextrin, galactose, protein and amino acids.
Br. J. Nutr. 110(5) , 848-55, (2013) The present study evaluated whether the inclusion of protein (PRO) and amino acids (AA) within a maltodextrin (MD) and galactose (GAL) recovery drink enhanced post-exercise liver and muscle glycogen repletion. A total of seven trained male cyclists completed ... |