(-)-catechin
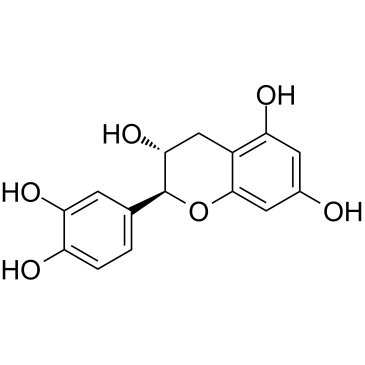
(-)-catechin structure
|
Common Name | (-)-catechin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 18829-70-4 | Molecular Weight | 290.26800 | |
| Density | 1.593 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 630.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H14O6 | Melting Point | 175-176ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 335ºC | |
|
An efficient and economical MTT assay for determining the antioxidant activity of plant natural product extracts and pure compounds.
J. Nat. Prod. 73 , 1193-5, (2010) Antioxidants scavenge free radicals, singlet oxygen, and electrons in cellular redox reactions. The yellow MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] is reduced to a purple formazan by mitochondrial enzymes. NADPH is the basis of esta... |
|
|
The blood pressure effect and related plasma levels of flavan-3-ols in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Food Funct. 6 , 3479-89, (2015) We studied the short-term antihypertensive effect of flavan-3-ols (-)-epicatechin, (+)-catechin and (-)-catechin, in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Plasma metabolites and the corresponding plasma antioxidant capacity were determined. All the assayed f... |
|
|
Galactolipids from Bauhinia racemosa as a new class of antifilarial agents against human lymphatic filarial parasite, Brugia malayi.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 50 , 230-5, (2012) Bioassay guided fractionation of ethanolic extract of the leaves of Bauhinia racemosa led to the isolation of galactolipid and catechin class of the compounds (1-7) from the most active n-butanol fraction (F4). Among the active galactolipids, 1 emerged as the... |
|
|
Catechin gallates are NADP+-competitive inhibitors of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and other enzymes that employ NADP+ as a coenzyme.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 16 , 3580-6, (2008) Recent studies have shown that glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is an effectual therapeutic target for metabolic disorders, including obesity and diabetes. In this study, we used in silico and conventional screening approaches to identify putative inh... |
|
|
Flavonoids as opioid receptor ligands: identification and preliminary structure-activity relationships.
J. Nat. Prod. 70 , 1278-82, (2007) Flavonoids have been recognized as the active ingredients of many medicinal plant extracts due to interactions with proteins via phenolic groups and low toxicity. Here, we report the investigation of the flavonoid core as a potential new scaffold for the deve... |
|
|
Tea catechins inhibit hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET kinase) activity in human colon cancer cells: kinetic and molecular docking studies.
J. Med. Chem. 52 , 6543-5, (2009) Most cancer deaths result from spread of the primary tumor to distant sites (metastasis). MET is an important protein for metastasis in multiple tumor types. Here we report on the ability of tea catechins to suppress MET activation in human colon cancer cells... |
|
|
Bioconversion of (-)-epicatechin, (+)-epicatechin, (-)-catechin, and (+)-catechin by (-)-epigallocatechin-metabolizing bacteria.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 789-94, (2015) Bioconversion of (-)-epicatechin (-EC), (+)-epicatechin (+EC), (-)-catechin (-C), and (+)-catechin (+C) by (-)-epigallocatechin (-EGC)-metabolizing bacteria, Adlercreutzia equolifaciens MT4s-5, Eggerthella lenta JCM 9979, and Flavonifractor plautii MT42, was ... |
|
|
Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum fatty acid biosynthesis: evaluation of FabG, FabZ, and FabI as drug targets for flavonoids.
J. Med. Chem. 49 , 3345-53, (2006) After the discovery of a potent natural flavonoid glucoside as a potent inhibitor of FabI, a large flavonoid library was screened against three important enzymes (i.e., FabG, FabZ, and FabI) involved in the fatty acid biosynthesis of P. falciparum. Although f... |
|
|
Potent inhibitor scaffold against Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18 , 1633-40, (2010) The protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas' disease, can infect the heart, causing cardiac arrest frequently followed by death. To treat this disease, a potential molecular drug target is T. cruzi trans-sialidase (TcTS). However, inhibitor... |
|
|
Sulfonamide chalcone as a new class of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 , 5514-6, (2005) Chalcones 1-20, a new class of glycosidase inhibitors, were synthesized, and their glycosidase inhibitory activities were investigated. Non-aminochalcones 1-12 had no inhibitory activity, however, aminochalcones 13-20 had strong glycosidase (alpha-glucosidase... |