Cytisine
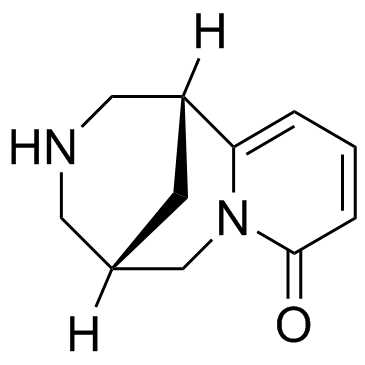
Cytisine structure
|
Common Name | Cytisine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 485-35-8 | Molecular Weight | 190.242 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 413.0±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H14N2O | Melting Point | 154-156ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 203.6±25.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Differential expression of the beta4 neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit affects tolerance development and nicotinic binding sites following chronic nicotine treatment.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 130 , 1-8, (2015) The role of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) containing the β4 subunit in tolerance development and nicotinic binding site levels following chronic nicotine treatment was investigated. Mice differing in expression of the β4-nAChR subunit [wi... |
|
|
Pharmacokinetics of cytisine, an α4 β2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist, in healthy smokers following a single dose.
Drug Test. Anal. , doi:10.1002/dta.1707, (2014) Cytisine, an α4 β2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist, is a plant alkaloid that is commercially extracted for use as a smoking cessation medication. Despite its long history of use, there is very little understanding of the pharmacokinetics of cytisine. To da... |
|
|
Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel 9- and 10-substituted cytisine derivatives. Nicotinic ligands of enhanced subtype selectivity.
J. Med. Chem. 49 , 2673-2676, (2006) We report the synthesis and pharmacological properties of several cytisine derivatives. Among them, two 10-substituted derivatives showed much higher selectivities for the alpha4beta2 nAChR subtype in binding assays than cytisine. The 9-vinyl derivative was f... |
|
|
3,5-Bicyclic aryl piperidines: a novel class of alpha4beta2 neuronal nicotinic receptor partial agonists for smoking cessation.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 , 4889-97, (2005) 3,5-Bicyclic aryl piperidines are a new class of high-affinity alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor agents. We have sought nicotinic receptor partial agonists of the alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor for smoking cessation, and a number of compounds fulfi... |
|
|
Artemin growth factor increases nicotinic cholinergic receptor subunit expression and activity in nociceptive sensory neurons.
Mol. Pain 10 , 31, (2014) Artemin (Artn), a member of the glial cell line-derived growth factor (GDNF) family, supports the development and function of a subpopulation of peptidergic, TRPV1-positive sensory neurons. Artn (enovin, neublastin) is elevated in inflamed tissue and its inje... |
|
|
In pursuit of alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor partial agonists for smoking cessation: carbon analogs of (-)-cytisine.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 , 2974-9, (2005) The preparation and biological activity of analogs of (-)-cytisine, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist, are discussed. All-carbon-containing phenyl ring replacements of the pyridone ring system, generated via Heck cyclization protocols, exhibit... |
|
|
Nicotine enhances inhibition of mouse vagal motor neurons by modulating excitability of premotor GABAergic neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarii.
J. Neurophysiol. 113(4) , 1165-74, (2015) The caudal nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) serves as the site of the first synapse for visceral sensory inputs to the central nervous system. The NTS sends functional projections to multiple brain nuclei, with gastric-related projections primarily targeti... |
|
|
Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: structural revelations, target identifications, and therapeutic inspirations.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 4705-45, (2005)
|
|
|
Cytisine--a tobacco treatment hiding in plain sight.
N. Engl. J. Med. 371(25) , 2429-30, (2014) A randomized, controlled trial published in this issue of the Journal brings renewed attention to cytisine, a potentially useful pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation that has been hiding in plain sight.1 A naturally occurring plant alkaloid, cytisine has bee... |
|
|
[Drugs used to treat nicotine addiction].
Prz. Lek. 69(10) , 1098-102, (2012) Tobacco smoking in Poland is fairly widespread on a large scale. Research suggests that the early twenty-first century, the percentage of female daily smokers aged 20 and above was 26%, and men the same age 43%. In addition, epidemiological studies have shown... |