Sultamicillin
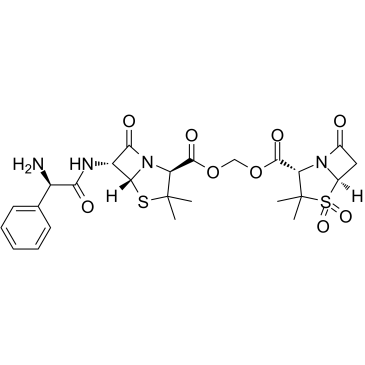
Sultamicillin structure
|
Common Name | Sultamicillin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 76497-13-7 | Molecular Weight | 594.657 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 907.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H30N4O9S2 | Melting Point | 190° | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 502.8±34.3 °C | |
|
Clinical response at Day 3 of therapy and economic outcomes in hospitalized patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection (ABSSSI).
Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 29(7) , 869-77, (2013) The FDA recently issued guidance for the types of infections that should be included in trials to support an indication for antibacterial treatment. The latest FDA guidance recommends assessing response to drug therapy at 48 to 72 hours as the primary endpoin... |
|
|
Antibiotic regimens for management of intra-amniotic infection.
Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 12 , CD010976, (2014) Chorioamnionitis is a common infection that affects both mother and infant. Infant complications associated with chorioamnionitis include early neonatal sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis. Chorioamnionitis can also result in maternal morbidity such as pelvic i... |
|
|
Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens-induced bacteremia in a healthy man.
Am. J. Emerg. Med. 32(7) , 812.e1-3, (2014) Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens is rarely associated with bacteremia but results in significant mortality. Almost all reported bacteremia cases have occurred in immunocompromised hosts, such as those with alcoholic liver disease, atherosclerosis, recent... |
|
|
In vitro pharmacodynamics of human-simulated exposures of ampicillin/sulbactam, doripenem and tigecycline alone and in combination against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.
J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 68(10) , 2296-304, (2013) Multidrug resistance is common among Acinetobacter baumannii, limiting the available options used to treat infections caused by this organism. The objective of this study was to compare monotherapy and combination therapy with ampicillin/sulbactam, doripenem ... |
|
|
Central line associated blood stream infection related to cooling catheter in cardiac arrest survivors undergoing therapeutic hypothermia by endovascular cooling.
Conn. Med. 77(1) , 35-41, (2013) The risk of central line associated blood stream infections (CLABSI) related to cooling catheters used for therapeutic hypothermia (TH) is unclear.We performed a retrospective analysis on 131 cardiac arrest survivors between 2007 and 2010, who underwent TH by... |
|
|
Evaluation of cutaneous palpebral anthrax.
Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 32(4) , 294-8, (2013) Anthrax is a rare disease caused by Bacillus anthracis. Antrax is zoonotic disease and is often encountered in persons engaged in animal husbandry. Cutaneous anthrax is approximately 95% of anthrax in humans. Palbebral involvement is rare.In this study, we ai... |
|
|
New insights in the production of aerosol antibiotics. Evaluation of the optimal aerosol production system for ampicillin-sulbactam, meropenem, ceftazidime, cefepime and piperacillin-tazobactam.
Int. J. Pharm. 455(1-2) , 182-8, (2013) Several aerosol antibiotics are on the market and several others are currently being evaluated. Aim of the study was to evaluate the aerosol droplet size of five different antibiotics for future evaluation as an aerosol administration.The nebulizers Sunmist(®... |
|
|
Use of ampicillin/sulbactam and sultamicillin in pediatric infections: a re-evaluation.
J. Int. Med. Res. 29(4) , 257-69, (2001) Ampicillin/sulbactam is an effective solution to the emergence of beta-lactamase-mediated resistance among common pediatric pathogens, and is a widely recognized treatment option for a variety of pediatric infections. Recent antimicrobial surveillance data co... |
|
|
Role of sultamicillin and ampicillin/sulbactam in the treatment of upper and lower bacterial respiratory tract infections.
Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 18(3) , 199-209, (2001) The emergence of beta-lactamase-mediated resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics among key respiratory tract pathogens has threatened the usefulness of the beta-lactam agents familiar to physicians as being clinically effective and well tolerated. This article ... |
|
|
Ampicillin/sulbactam: its potential use in treating infections in critically ill patients.
Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 42(5) , 384-9, (2013) The purpose of this paper was to review the potential utility of ampicillin/sulbactam (SAM) as a therapy for serious infections in critically ill patients. Data for this review were identified by searches of PubMed and of the reference lists of the included a... |