Riboflavin-5-phosphate sodium
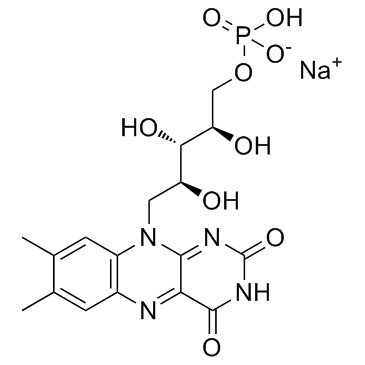
Riboflavin-5-phosphate sodium structure
|
Common Name | Riboflavin-5-phosphate sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 130-40-5 | Molecular Weight | 478.326 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H20N4NaO9P | Melting Point | >300°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Femtosecond dynamics of short-range protein electron transfer in flavodoxin.
Biochemistry 52(51) , 9120-8, (2013) Intraprotein electron transfer (ET) in flavoproteins is important for understanding the correlation of their redox, configuration, and reactivity at the active site. Here, we used oxidized flavodoxin as a model system and report our complete characterization ... |
|
|
[Experimental evaluation of reamberin and cytoflavin effects on the course and outcome of acute burn injury].
Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 76(4) , 39-44, (2013) Survival rate, average life expectancy of victims, parameters of the acid - base balance, gas composition of blood, and morphological structure of internal organs have been studied in acute experiments on a group of 120 rats with burn injury of IIIB degree (2... |
|
|
[Protective effect of cytoflavin and its components in mice with acute alloxan intoxication].
Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 76(4) , 26-31, (2013) We have studied the protective effect of cytoflavin and its components (meglumine sodium succinate, riboflavin, inosine and nicotinamide) in mice with acute alloxan intoxication. It is established that cytoflavin and its components possessing in vitro antioxi... |
|
|
Rho and RNase play a central role in FMN riboswitch regulation in Corynebacterium glutamicum.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43(1) , 520-9, (2015) Riboswitches are RNA elements that regulate gene expression in response to their ligand. Although these regulations are thought to be performed without any aid of other factors, recent studies suggested the participation of protein factors such as transcripti... |
|
|
Controllable coating of microneedles for transdermal drug delivery.
Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41(3) , 415-22, (2015) Coated microneedles have been paid much attention recently, and several coating strategies have been developed to address the problems during coating process. However, there are still some unresolved issues, such as, precise control requirements, microneedle ... |
|
|
The crystal structure of Pseudomonas putida azoreductase - the active site revisited.
FEBS J. 280(24) , 6643-57, (2013) The enzymatic degradation of azo dyes begins with the reduction of the azo bond. In this article, we report the crystal structures of the native azoreductase from Pseudomonas putida MET94 (PpAzoR) (1.60 Å), of PpAzoR in complex with anthraquinone-2-sulfonate ... |
|
|
Gene Regulation by Riboswitches with and without Negative Feedback Loop
Biophys. J. 103(11) , 2320-30, (2012) Riboswitches, structured elements in the untranslated regions of messenger RNAs, regulate gene expression by binding specific metabolites. We introduce a kinetic network model that describes the functions of riboswitches at the systems level. Using experiment... |
|
|
Differential calmodulin-modulatory and electron transfer properties of neuronal nitric oxide synthase mu compared to the alpha variant.
FEBS Lett. 587(24) , 3973-8, (2013) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase μ (nNOSμ) contains 34 additional residues in an autoregulatory element compared to nNOSα. Cytochrome c and flavin reductions in the absence of calmodulin (CaM) were faster in nNOSμ than nNOSα, while rates in the presence of CaM ... |
|
|
Intra- and inter-molecular effects of a conserved arginine residue of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthases on FMN and calmodulin binding.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 533(1-2) , 88-94, (2013) Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule, from l-arginine, utilizing electrons from NADPH. NOSs are flavo-hemo proteins, with two flavin molecules (FAD and FMN) and one heme per monomer, which require the binding of cal... |
|
|
Structural characterization of HP1264 reveals a novel fold for the flavin mononucleotide binding protein.
Biochemistry 52(9) , 1583-93, (2013) Complex I (NADH-quinone oxidoreductase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the initial electron transfer from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) to flavin mononucleotide (FMN) bound at the tip of the hydrophilic domain of complex I. The electron flow into comp... |