N-(3-Hydroxytetradecanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone
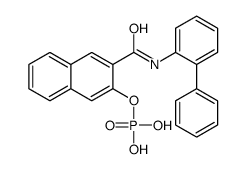
N-(3-Hydroxytetradecanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone structure
|
Common Name | N-(3-Hydroxytetradecanoyl)-DL-homoserine lactone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 172670-99-4 | Molecular Weight | 327.45900 | |
| Density | 1.04±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | Boiling Point | 549.3±50.0 °C(Predicted) | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H33NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Quorum sensing and biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans.
Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 631 , 178-88, (2008) Streptococcus mutans is the primary causative agent involved in dental caries in humans. Among important virulence factors of this pathogen, its ability to form and sustain a polysaccharide-encased biofilm (commonly called dental plaque) is vital not only to ... |
|
|
Quorum sensing in bacteria.
Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55 , 165-99, (2001) Quorum sensing is the regulation of gene expression in response to fluctuations in cell-population density. Quorum sensing bacteria produce and release chemical signal molecules called autoinducers that increase in concentration as a function of cell density.... |
|
|
Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing.
Annu. Rev. Genet. 35 , 439-68, (2001) Quorum sensing is an example of community behavior prevalent among diverse bacterial species. The term "quorum sensing" describes the ability of a microorganism to perceive and respond to microbial population density, usually relying on the production and sub... |
|
|
Small talk. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria.
Cell 109(4) , 421-4, (2002) In a process called quorum sensing, groups of bacteria communicate with one another to coordinate their behavior and function like a multicellular organism. A diverse array of secreted chemical signal molecules and signal detection apparatuses facilitate high... |
|
|
Listening in on bacteria: acyl-homoserine lactone signalling.
Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3(9) , 685-95, (2002) Bacterial cell-to-cell signalling has emerged as a new area in microbiology. Individual bacterial cells communicate with each other and co-ordinate group activities. Although a lot of detail is known about the mechanisms of a few well-characterized bacterial ... |
|
|
Acyl homoserine-lactone quorum-sensing signal generation.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96 , 4360, (1999) Acyl homoserine lactones (acyl-HSLs) are important intercellular signaling molecules used by many bacteria to monitor their population density in quorum-sensing control of gene expression. These signals are synthesized by members of the LuxI family of protein... |
|
|
Antimicrobial enzymes: an emerging strategy to fight microbes and microbial biofilms.
Biotechnol. J. 8(1) , 97-109, (2013) With the increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistance, antimicrobial enzymes aimed at the disruption of bacterial cellular machinery and biofilm formation are under intense investigation. Several enzyme-based products have already been commercialized for ap... |
|
|
Quo vadis quorum quenching?
Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 13(5) , 688-98, (2013) With the emergence of microbial pathogens increasingly resistant against commonly used antibiotics, new treatment strategies are desperately needed. Bacterial quorum sensing has attracted a lot of attention over the last decade as a potential new target for a... |
|
|
Small molecules that modulate quorum sensing and control virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
J. Org. Chem. 75(20) , 6737-46, (2010) Bacteria use small molecule signals to access their local population densities in a process called quorum sensing (QS). Once a threshold signal concentration is reached, and therefore a certain number of bacteria have assembled, bacteria use QS to change gene... |
|
|
A fatty acid messenger is responsible for inducing dispersion in microbial biofilms.
J. Bacteriol. 191(5) , 1393-403, (2009) It is well established that in nature, bacteria are found primarily as residents of surface-associated communities called biofilms. These structures form in a sequential process initiated by attachment of cells to a surface, followed by the formation of matri... |