CP-66248
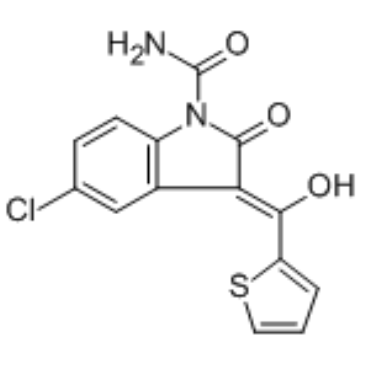
CP-66248 structure
|
Common Name | CP-66248 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 120210-48-2 | Molecular Weight | 320.75 | |
| Density | 1.58g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 523.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H9ClN2O3S | Melting Point | 230° (dec) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 270.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Tenidap decreases IL-8 and monocyte chemotactic peptide-1 (MCP-1) mRNA expression in the synovial tissue of rabbits with antigen arthritis and in cultured synovial cells.
Clin. Exp. Immunol. 111(3) , 588-96, (1998) Since IL-8 and MCP-1 are chemoattractant proteins that participate in the recruitment of inflammatory cells into the arthritic joint, we examined the effects of tenidap, a new anti-inflammatory drug of the oxindole family, on IL-8 and MCP-1 expression in the ... |
|
|
The renal Na-HCO3-cotransporter expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes: inhibition by tenidap and benzamil and effect of temperature on transport rate and stoichiometry.
Pflugers Arch. 442(5) , 709-17, (2001) In the present experiments we expressed the rat kidney Na+-HCO3- cotransporter (rkNBC) in Xenopus laevis oocytes to reinvestigate the flux coupling ratio under improved measuring conditions. Essentially the current/voltage (I/V) relationship of isolated insid... |
|
|
Tenidap: not just another NSAID?
Ann. Rheum. Dis. 55(2) , 79-82, (1996)
|
|
|
Tenidap, an anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits DNA and collagen syntheses, depresses cell proliferation, and lowers intracellular pH in cultured human gingival fibroblasts.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 300(2) , 668-72, (2002) The effect of tenidap [(+/-)-5-chloro-2,3-dihydro-3-(hydroxy-2-thienylmethylene)-2-oxo-1H-indole-1-carboxamide], a new anti-inflammatory agent, was investigated on DNA synthesis by means of [(3)H]thymidine incorporation, collagen synthesis by means of [(3)H]p... |
|
|
Tenidap enhances P2Z/P2X7 receptor signalling in macrophages.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 355(2-3) , 235-44, (1998) Tenidap is an anti-inflammatory drug whose mechanism of action is not fully understood. It has been shown to block plasma membrane anion transport and to decrease release of interleukin-1beta, probably via the inhibition of interleukin-1beta converting enzyme... |
|
|
Tenidap, a novel anti-inflammatory agent, is an opener of the inwardly rectifying K+ channel hKir2.3.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 435(2-3) , 153-60, (2002) We studied the effect of a novel anti-inflammatory agent, tenidap, on a cloned inwardly rectifying K+ channel, hKir2.3. Tenidap (a) potently potentiated 86Rb+ efflux through hKir2.3 channels expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells (EC50=402 nM), (b) reversib... |
|
|
A pharmacokinetic model for tenidap in normal volunteers and rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Pharm. Res. 16(10) , 1608-15, (1999) To develop a pharmacokinetic model for tenidap and to identify important relationships between the pharmacokinetic parameters and available covariates.Plasma concentration data from several phase I and phase II studies were used to develop a pharmacokinetic m... |
|
|
Interaction between cAMP, volume‑regulated anion channels and the Na+‑HCO3‑‑cotransporter, NBCe1, in the regulation of nutrient‑ and hypotonicity‑induced insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets and tumoral insulin‑producing BRIN‑BD11 cells.
Mol. Med. Report. 7(5) , 1666-72, (2013) Soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC) has been hypothesized to play a role in insulin secretion. The present study aimed to investigate the interaction between adenosine 3',5'‑cyclic monophosphate (cAMP), volume‑regulated anion channels (VRACs) and the electrogenic ... |
|
|
Tenidap: a novel cytokine-modulating antirheumatic drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Scand. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 100 , 31-44, (1994) Tenidap is a novel, once-daily, cytokine modulating antirheumatic drug indicated for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In vitro, tenidap significantly inhibits the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumour... |
|
|
Functional characterization of Cl-/HCO3- exchange in villous cells of the mouse ileum.
Biomed. Res. 27(6) , 265-74, (2006) At least three kinds of Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) exchangers, SLC26A3, SLC26A6 and AE2, have been demonstrated to be expressed in the intestinal epithelial cell. To examine the functional expression of these exchangers in the native enterocyte, we studied the Cl(-)/HCO... |