SKF 100398
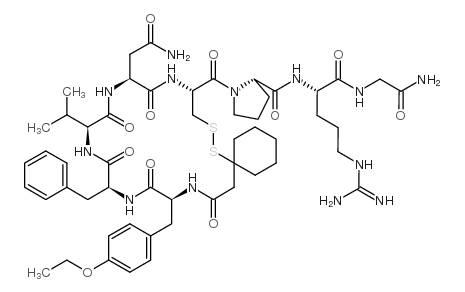
SKF 100398 structure
|
Common Name | SKF 100398 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 77453-01-1 | Molecular Weight | 1136.39000 | |
| Density | 1.44g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C53H77N13O11S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Vasopressin increases water permeability of kidney collecting duct by inducing translocation of aquaporin-CD water channels to plasma membrane.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92(4) , 1013-7, (1995) Water excretion by the kidney is regulated by the peptide hormone vasopressin. Vasopressin increases the water permeability of the renal collecting duct cells, allowing more water to be reabsorbed from collecting duct urine to blood. Despite long-standing int... |
|
|
Arginine vasopressin enhances pHi regulation in the presence of HCO3- by stimulating three acid-base transport systems.
Nature 337(6208) , 648-51, (1989) Growth factors raise intracellular pH (pHi) by stimulating Na+/H+ exchange in the absence of HCO3-. In mutant cells that lack the Na+/H+ exchange activity, this alkalinization does not occur, and the cells do not proliferate without artificial elevation of pH... |
|
|
Pharmacological characterization of V1a vasopressin receptors in the rat cortical collecting duct.
Am. J. Physiol. 262 , F546-F553, (1992) Vasopressin receptors in distal segments of the rat nephron were identified in isolated tubules using two labeled ligands: the [1-(beta-mercapto-beta,beta-cyclopentamethylenepropionic acid), 2-(O-methyl)tyrosine,4-threonine,8-ornithine,9-125I-tyrosylamide]- v... |
|
|
Neuronal cell bodies in paraventricular nucleus affect renal hemodynamics and excretion via the renal nerves.
Am. J. Physiol. 275 , R1334-R1342, (1998) Several lines of evidence support the existence of an oligosynaptic projection from the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) to the kidney in the rat. We sought to provide evidence that this neural pathway is capable of influencing renal function... |
|
|
Intracisternally applied angiotensin II does not excite reticulospinal vasomotor neurons in anesthetized rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 304(1-3) , 63-71, (1996) We examined whether vasomotor neurons in the rostroventrolateral reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata might be responsible for an acute increase in arterial pressure, elicited by application of angiotensin II in the central nervous system, as suggested ... |
|
|
Effect of peripheral injection of arginine vasopressin and its receptor antagonist on burn shock in the rat.
Neuropeptides 17(1) , 17-22, (1990) To investigate the effect of arginine vasopressin (AVP) in the peripheral circulation on burn shock in the rat, AVP and its nonselective V1/V2 receptor antagonist d(CH2)5Tyr (Et)VAVP were administered intravenously in burn shocked rats. Cardiovascular paramet... |
|
|
V1 vs. combined V1+V2 vasopressin blockade after hemorrhage in conscious dogs.
Am. J. Physiol. 255(6 Pt 2) , H1325-9, (1988) We examined the hypothesis that V2-like receptors might contribute to the hemodynamic response seen after blockade of the vasoconstrictor (V1) effect of arginine vasopressin (AVP) in nonhypotensive hemorrhage. Seven chronically instrumented dogs were bled 15 ... |
|
|
Effects of a vasopressin antagonist with combined antipressor and antiantidiuretic activities in rats with left ventricular dysfunction.
Circulation 81(1) , 308-11, (1990) These experiments assessed the hemodynamic and aquaretic effects of an arginine vasopressin (AVP) antagonist with dual V1V2-receptor inhibiting properties in rats with congestive heart failure resulting from ischemic cardiomyopathy. The compound d(CH2)5-D-Tyr... |
|
|
Support of arterial blood pressure by major pressor systems in conscious dogs.
Am. J. Physiol. 255(3 Pt 2) , H483-91, (1988) The roles of the autonomic nervous system, vasopressin, and angiotensin II in support of blood pressure were evaluated in seven conscious, resting dogs while hydrated or dehydrated. Mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) was monitored, and the dogs were given hex... |
|
|
Receptors with V1 characteristics mediate the maintenance of ethanol tolerance by vasopressin.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 247(2) , 536-41, (1988) The neurohypophyseal hormone arginine vasopressin (AVP) acts in the central nervous system (CNS) to maintain functional tolerance to several effects of ethanol. The ability of exogenous vasopressin (administered i.c.v.) to maintain tolerance to the hypnotic e... |