Sodium (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-icosatetraenoate
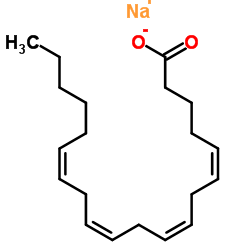
Sodium (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-icosatetraenoate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-icosatetraenoate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6610-25-9 | Molecular Weight | 326.449 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 407.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H31NaO2 | Melting Point | -49.5ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 336.3ºC | |
|
GC/TOFMS analysis of metabolites in serum and urine reveals metabolic perturbation of TCA cycle in db/db mice involved in diabetic nephropathy.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 304(11) , F1317-24, (2013) Early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy (DN) is difficult although it is of crucial importance to prevent its development. To probe potential markers and the underlying mechanism of DN, an animal model of DN, the db/db mice, was used and serum and urine metab... |
|
|
Hinokitiol inhibits platelet activation ex vivo and thrombus formation in vivo
Biochem. Pharmacol. 85(10) , 1478-85, (2013) Hinokitiol is a tropolone-related bioactive compound that has been used in hair tonics, cosmetics, and food as an antimicrobial agent. Recently, hinokitiol has attracted considerable interest because of its anticancer activities. Platelet activation plays a c... |
|
|
Pre-existent asymmetry in the human cyclooxygenase-2 sequence homodimer.
J. Biol. Chem. 288(40) , 28641-55, (2013) Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase-2 (PGHS-2), also known as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), is a sequence homodimer. However, the enzyme exhibits half-site heme and inhibitor binding and functions as a conformational heterodimer having a catalytic subunit (Ecat... |
|
|
Fenretinide prevents inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of allergic asthma.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 51(6) , 783-92, (2014) Arachidonic acid (AA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) play important roles in inflammation and disease progression, where AA is viewed as proinflammatory and DHA as antiinflammatory. We observe in our model of allergic asthma that the AA/DHA ratio is significa... |
|
|
Characterisation of the prostaglandin E2-ethanolamide suppression of tumour necrosis factor-α production in human monocytic cells
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1831(6) , 1098-107, (2013) Background and purpose Prostaglandin ethanolamides or prostamides are naturally occurring neutral lipid derivatives of prostaglandins that have been shown to be synthesised in vivo following COX-facilitated oxygenation of arachidonoyl ethanolamine (anandamide... |
|
|
Application of ANS fluorescent probes to identify hydrophobic sites on the surface of DREAM.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1844(9) , 1472-80, (2014) DREAM (calsenilin or KChIP-3) is a calcium sensor involved in regulation of diverse physiological processes by interactions with multiple intracellular partners including DNA, Kv4 channels, and presenilin, however the detailed mechanism of the recognition of ... |
|
|
Assessment of platelet function with light transmission aggregometry in 24 patients supported with a continuous-flow left ventricular assist device: a single-center experience.
J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 148(6) , 3119-25.e1, (2014) This study evaluated platelet function for an extended period of time in patients with a HeartMate II continuous-flow left ventricular assist device (Thoratec Corporation, Pleasanton, Calif) with light transmission aggregometry and investigated the potential ... |
|
|
Role of ion channels and subcellular Ca2+ signaling in arachidonic acid-induced dilation of pressurized retinal arterioles.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55(5) , 2893-902, (2014) To investigate the mechanisms responsible for the dilatation of rat retinal arterioles in response to arachidonic acid (AA).Changes in the diameter of isolated, pressurized rat retinal arterioles were measured in the presence of AA alone and following pre-inc... |
|
|
Mechanisms of aspirin-intolerant asthma: identifying inflammatory pathways in the pathogenesis of asthma.
Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 163(1) , 1-2, (2014)
|
|
|
Metabolic conversion of intra-amniotically-injected deuterium-labeled essential fatty acids by fetal rats following maternal n-3 fatty acid deficiency.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1841(9) , 1336-44, (2014) Accumulation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in the fetal brain is accomplished predominantly via a highly selective flow of docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3, DHA) and arachidonic acid (20:4n-6, AA) through the placenta. Little is known regarding the endog... |