L-Lactic acid
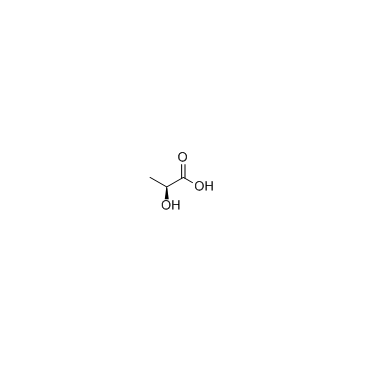
L-Lactic acid structure
|
Common Name | L-Lactic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 79-33-4 | Molecular Weight | 90.078 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 227.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O3 | Melting Point | 52-54°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 109.9±16.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS05 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Physiology and pathophysiology of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid.
J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 16(4) , 648-69, (1993) Concentrations of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) appear to be directly dependent upon their rate of production in the brain. There is evidence that the net release of short-chain monocarboxylic acids from the brain is a major route for removing th... |
|
|
The human serum metabolome.
PLoS ONE 6(2) , e16957, (2011) Continuing improvements in analytical technology along with an increased interest in performing comprehensive, quantitative metabolic profiling, is leading to increased interest pressures within the metabolomics community to develop centralized metabolite ref... |
|
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population.
Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994) Organic acid concentrations were quantified by gas chromatography and the individual acids identified by mass spectrometry in urine specimens from a healthy Turkish pediatric population of ages 2 days to 16 years, subdivided into five age groups. We quantifie... |
|
|
Use of high-resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for rapid multi-component analysis of urine.
Clin. Chem. 30(3) , 426-32, (1984) Numerous low-Mr metabolites--including creatinine, citrate, hippurate, glucose, ketone bodies, and various amino acids--have been identified in 400- and 500-MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectra of intact human urine. The presence of many of ... |
|
|
Automated screening of urine samples for carbohydrates, organic and amino acids after treatment with urease.
J. Chromatogr. A. 562(1-2) , 125-38, (1991) Eighty-five clinical urine samples and nineteen urine samples previously found by other laboratories to suggest genetic metabolic defects were prepared for trimethylsilylation by treatment with urease, followed by azeotropic dehydration. The "Target Analyte S... |
|
|
Quantitative analysis for organic acids in biological samples: batch isolation followed by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis.
Clin. Chem. 35(4) , 587-95, (1989) This new method for qualitative and quantitative determination of organic acids, aldehydes, and ketones in biological samples is effective for use with urine, plasma, and amniotic fluid, and it requires no deproteinization. Isolation by batch-wise liquid part... |
|
|
Gender-related and age-related urinalysis of healthy subjects by NMR-based metabonomics.
NMR Biomed. 21(3) , 195-207, (2008) NMR-based metabonomic analysis is a well-established approach to characterizing healthy and diseased states. The aim of this study was to investigate inter-individual variability in the metabolic urinary profile of a healthy Greek population, not subjected to... |
|
|
Intracellular flux analysis applied to the effect of dissolved oxygen on hybridomas.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 44(1-2) , 27-36, (1995) Quantitative estimates of intracellular fluxes and measurements of intracellular concentrations were used to evaluate the effect of dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration on CRL 1606 hybridoma cells in batch culture. The estimates of intracellular fluxes were ge... |
|
|
The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 871(2) , 164-73, (2008) With continuing improvements in analytical technology and an increased interest in comprehensive metabolic profiling of biofluids and tissues, there is a growing need to develop comprehensive reference resources for certain clinically important biofluids, suc... |