Salvianolic acid A
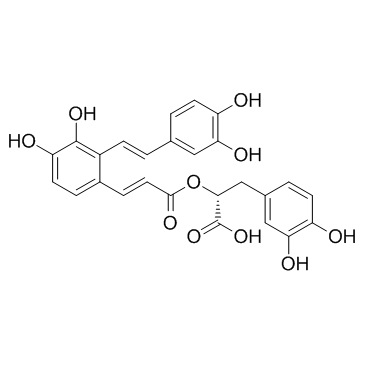
Salvianolic acid A structure
|
Common Name | Salvianolic acid A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96574-01-5 | Molecular Weight | 494.447 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 858.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H22O10 | Melting Point | 164-167ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 292.9±27.8 °C | |
|
Surfactant-coated graphitized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as the pseudostationary phase in electrokinetic chromatography for the analysis of phytochemical compounds in biological fluids.
Electrophoresis 36(7-8) , 1055-63, (2015) This report describes the use of surfactant-coated graphitized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (SC-GMWNTs) as a novel pseudostationary phase in CE with diode array detection for the determination of phenolic acids and tanshinones in herbal and urine samples. Sev... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of six phenolic constituents of Danshen injection in rat plasma by LC-ESI-MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.
Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. (Chichester, Eng.) 17(4) , 395-403, (2011) Salvianolic acid A, salvianolic acid B, danshensu, protocatechuic aldehyde, rosmarinic acid and lithospermic acid are the six major active constituents in Danshen injection. In this study, a rapid, sensitive and specific liquid chromatographic-electrospray io... |
|
|
In silico analysis and experimental validation of molecular mechanisms of salvianolic acid A-inhibited LPS-stimulated inflammation, in RAW264.7 macrophages.
Cell Prolif. 46(5) , 595-605, (2013) The aim of this study was to explore mechanisms by which salvianolic acid A (SAA) revealed its anti-inflammatory activity, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.Nitric oxide (NO) concentration was determined by the Griess reaction and cell via... |
|
|
The caffeic acid in aqueous extract of Tournefortia sarmentosa enhances neutrophil phagocytosis of Escherichia coli.
Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 36(6) , 390-6, (2014) Tournefortia sarmentosa, a Chinese herbal medicine, is considered an antioxidant or a detoxicating agent. Recently T. sarmentosa has received attention for its effects on the immune response. Here we provide evidence that aqueous extract of T. sarmentosa can ... |
|
|
[Chemical constituents of Salvia chinensis].
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 38(10) , 1556-9, (2013) Chemical constituents were investigated on the ethyl acetate extract of Salvia chinensis. Compounds were separated and purified by various chromatograhic techniques including silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 and reversed-phase HPLC. Their structures were identified... |
|
|
System-level multi-target drug discovery from natural products with applications to cardiovascular diseases.
Mol. Divers. 18(3) , 621-35, (2014) The term systems pharmacology describes a field of study that uses computational and experimental approaches to broaden the view of drug actions rooted in molecular interactions and advance the process of drug discovery. The aim of this work is to stick out t... |
|
|
Effects of salvianolic scid A on plantar microcirculation and peripheral nerve function in diabetic rats
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 665(1-3) , 40-6, (2011) Salvianolic acid A (SalA) is the main efficacious, water-soluble constituent of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. This study evaluated the effects of SalA on plantar microcirculation and peripheral nerve dysfunction in streptozotocin (STZ )-induced type 2 diabetic r... |
|
|
Salvianolic acid A protects against vascular endothelial dysfunction in high-fat diet fed and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 13(10) , 884-94, (2011) Salvianolic acid A (SalA) is one of the main active ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhizae. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of SalA on the diabetic vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED). The rats were given a high-fat and high-sucrose die... |
|
|
Salvianolic acid A protects human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against H2O2-induced injury by increasing stress tolerance ability
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 421(3) , 479-83, (2012) Highlights ► Sal A inhibits the activation of AMPK. ► Sal A inhibits the activation of Akt. ► The protective effects of Sal A are related to stress tolerance via inhibition of AMPK and Akt. |
|
|
Salvianolic acid A inhibits angiotensin II-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by attenuating the production of ROS.
Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 33(1) , 41-8, (2012) To investigate the action of salvianolic acid A (SalA) on angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and the possible signaling pathways mediating this action.Cell proliferation was examined with MTT assay... |