Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide
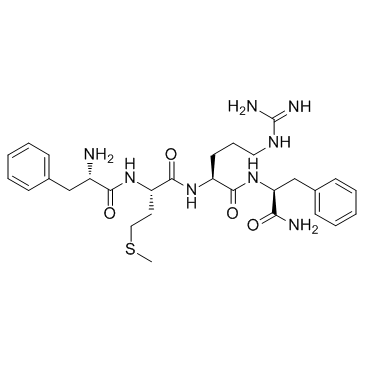
Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide structure
|
Common Name | Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64190-70-1 | Molecular Weight | 598.76000 | |
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H42N8O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Persistent long-term facilitation at an identified synapse becomes labile with activation of short-term heterosynaptic plasticity.
J. Neurosci. 34(14) , 4776-85, (2014) Short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity are cellular correlates of learning and memory of different durations. Little is known, however, how these two forms of plasticity interact at the same synaptic connection. We examined the reciprocal impact of shor... |
|
|
Some aspects of the immunolocalization of FMRFamide in the nervous system of turbellarians, Polycelis tenuis and Girardia tigrina. Short communication.
Acta Biol. Hung. 63 Suppl 2 , 83-7, (2012) The details of the morphology of the nervous system has been investigated in two turbellarian species Polycelis tenuis and Girardia tigrina using confocal laser scanning microscopy and immunostaining to neuropeptide FMRFamide. Abundant FMRFamide immunoreactiv... |
|
|
Seven up acts as a temporal factor during two different stages of neuroblast 5-6 development.
Development 138(24) , 5311-20, (2011) Drosophila embryonic neuroblasts generate different cell types at different time points. This is controlled by a temporal cascade of Hb→Kr→Pdm→Cas→Grh, which acts to dictate distinct competence windows sequentially. In addition, Seven up (Svp), a member of th... |
|
|
Novel insights into the echinoderm nervous system from histaminergic and FMRFaminergic-like cells in the sea cucumber Leptosynapta clarki.
PLoS ONE 7(9) , e44220, (2012) Understanding of the echinoderm nervous system is limited due to its distinct organization in comparison to other animal phyla and by the difficulty in accessing it. The transparent and accessible, apodid sea cucumber Leptosynapta clarki provides novel opport... |
|
|
FMRF-amide immunoreactivity pattern in the planula and colony of the hydroid Gonothyraea loveni.
Zoology (Jena.) 116(1) , 9-19, (2013) Gonothyraea loveni (Allman, 1859) is a colonial thecate hydrozoan with a life cycle that lacks a free-swimming medusa stage. The development from zygote to planula occurs within meconidia attached to the female colony. The planula metamorphosis results in the... |
|
|
Targeting a neuropeptide to discrete regions of the motor arborizations of a single neuron.
J. Exp. Biol. 215(Pt 12) , 2108-16, (2012) The heart excitor (HE) motor neuron in the leech Hirudo releases acetylcholine (ACh) and a peptide, FMRFamide, to regulate the contractile activity of the heart tube and associated side vessels. Consistent with Dale's principle, it was assumed that both neuro... |
|
|
Klumpfuss controls FMRFamide expression by enabling BMP signaling within the NB5-6 lineage.
Development 140(10) , 2181-9, (2013) A number of transcription factors that are expressed within most, if not all, embryonic neuroblast (NB) lineages participate in neural subtype specification. Some have been extensively studied in several NB lineages (e.g. components of the temporal gene casca... |
|
|
The neuromuscular system in freshwater furcocercaria from Belarus. II Diplostomidae, Strigeidae, and Cyathocotylidae.
Parasitol. Res. 110(2) , 583-92, (2012) The neuromuscular system (NMS) in cercariae of Diplostomum pseudospathaceum, Cotylurus szidati, Australapatemon burti, Holostephanus volgensis, and Paracoenogonimus ovatus was studied with immunocytochemical methods and confocal scanning laser microscopy. The... |
|
|
The neuro-muscular system in fresh-water furcocercaria from Belarus. I Schistosomatidae.
Parasitol. Res. 110(1) , 185-93, (2012) The neuro-muscular system (NMS) in cercariae of the family Schistosomatidae from Belarus was studied with immunocytochemical methods and confocal scanning laser microscopy. The specimens of Bilharziella polonica were compared with Trichobilharzia szidati and ... |
|
|
Innervation of bivalve larval catch muscles by serotonergic and FMRFamidergic neurons.
Acta Biol. Hung. 63 Suppl 2 , 221-9, (2012) Bivalve larvae use catch muscles for rapid shell closure and maintenance of the closed condition. We used specific antibodies against the muscle proteins together with phalloidin and neuronal markers, FMRFamide and serotonin (5-HT), to analyze mutual distribu... |