Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide
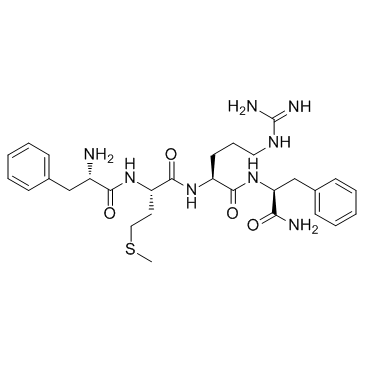
Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide structure
|
Common Name | Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64190-70-1 | Molecular Weight | 598.76000 | |
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H42N8O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amidePhe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide dose dependently (ED50=23 nM) activates a K+ current in the peptidergic caudodorsal neurons. |
| Name | fmrf amide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide dose dependently (ED50=23 nM) activates a K+ current in the peptidergic caudodorsal neurons. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ED50: 23 nM (K+ current)[1] |
| In Vitro | In the molluscan central nervous system, Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide (FMRFa) acts on K+ channels in sensory, motor-, and neuroendocrine neurones. Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide activates a novel K+ current that is characterized by a combined voltage- and receptor-dependent gating mechanism, with both factors being necessary for opening of the channels[1]. Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide (1 μM) significantly inhibits glucose stimulated (300 mg/dL) insulin release (p<0.005) and somatostatin release (p<0.01) from the isolated perfused pancreas. Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide (FMRF-NH2) (1 and 10 μM) is without effect on glucagon secretion, either in low glucose (50 mg/dL), high glucose (300 mg/dL), or during arginine stimulation (5 mM)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide (FMRFamide) stimulates growth hormone secretion in conscious OVX rats. The presence of Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide-like immunoreactivity in neuronal elements in the hypothalamus suggested a role for this in the hypothalamic control of the anterior pituitary function. The injection of 200 ng (313.8 picomoles) of FMRFamide (in 2 uL) produces a significantly increased plasma GH 15 min after injection. The GH-increasing effect of 400-800 ng (627-1255 picomoles) of FMRFamide is already developed after 5 min and lasted up to 30 min[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H42N8O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 598.76000 |
| Exact Mass | 598.30500 |
| PSA | 243.61000 |
| LogP | 3.51940 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Persistent long-term facilitation at an identified synapse becomes labile with activation of short-term heterosynaptic plasticity.
J. Neurosci. 34(14) , 4776-85, (2014) Short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity are cellular correlates of learning and memory of different durations. Little is known, however, how these two forms of plasticity interact at the same syn... |
|
|
Some aspects of the immunolocalization of FMRFamide in the nervous system of turbellarians, Polycelis tenuis and Girardia tigrina. Short communication.
Acta Biol. Hung. 63 Suppl 2 , 83-7, (2012) The details of the morphology of the nervous system has been investigated in two turbellarian species Polycelis tenuis and Girardia tigrina using confocal laser scanning microscopy and immunostaining ... |
|
|
Seven up acts as a temporal factor during two different stages of neuroblast 5-6 development.
Development 138(24) , 5311-20, (2011) Drosophila embryonic neuroblasts generate different cell types at different time points. This is controlled by a temporal cascade of Hb→Kr→Pdm→Cas→Grh, which acts to dictate distinct competence window... |
| phenylalanyl-methionyl-arginyl-phenylalaninamide |
| Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 |
| L-Phe-L-Met-L-Arg-L-Phe-NH2 |
| L-PHE-MET |
| phe-met |
| Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-amide |
| H-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 |
| L-Phe-L-Met |
| L-PHENYLALANYL-L-METHIONINE |
| Phe-Met-Arg-Phe, amide |
 CAS#:123197-28-4
CAS#:123197-28-4 CAS#:13734-34-4
CAS#:13734-34-4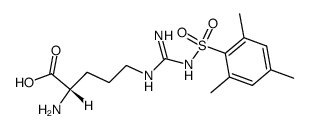 CAS#:58810-06-3
CAS#:58810-06-3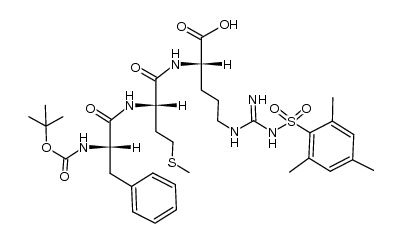 CAS#:123197-27-3
CAS#:123197-27-3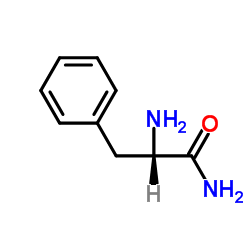 CAS#:5241-58-7
CAS#:5241-58-7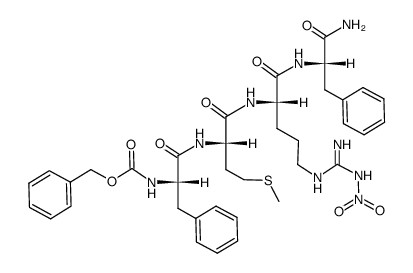 CAS#:85642-22-4
CAS#:85642-22-4 CAS#:2488-15-5
CAS#:2488-15-5