Dimethyl Carbonate
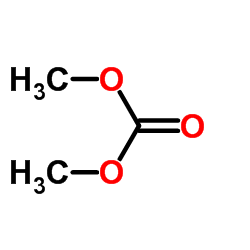
Dimethyl Carbonate structure
|
Common Name | Dimethyl Carbonate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 616-38-6 | Molecular Weight | 90.078 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 90.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O3 | Melting Point | 2-4 ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 18.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS02 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Do we need covalent bonding of Si nanoparticles on graphene oxide for Li-ion batteries?
Faraday Discuss. 173 , 391-402, (2014) In this manuscript, we report our investigation of anode materials for Li-ion batteries based on silicon-graphene oxide composites. Previous reports in the literature on silicon-graphene oxide (GO) composites as anodes have shown a large discrepancy between t... |
|
|
Antimicrobial and antioxidant amphiphilic random copolymers to address medical device-centered infections.
Acta Biomater. 22 , 131-40, (2015) Microbial biofilms are known to support a number of human infections, including those related to medical devices. This work is focused on the development of novel dual-function amphiphilic random copolymers to be employed as coatings for medical devices. Part... |
|
|
Self-Assembly of Catecholic Moiety-Containing Cationic Random Acrylic Copolymers.
J. Phys. Chem. B 119 , 8369-79, (2015) Amphiphilic polyelectrolytes (APEs), exhibiting particular self-association properties in aqueous media, can be used in different industrial applications, including drug delivery systems. Their typical core-shell structure (micelle) depends on the balance of ... |
|
|
Porous PLGA microspheres tailored for dual delivery of biomolecules via layer-by-layer assembly.
J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 103(5) , 1849-63, (2015) Tissue engineering is a complex and dynamic process that requires varied biomolecular cues to promote optimal tissue growth. Consequently, the development of delivery systems capable of sequestering more than one biomolecule with controllable release profiles... |
|
|
A novel method for differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into smooth muscle-like cells on clinically deliverable thermally induced phase separation microspheres.
Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 21(4) , 404-12, (2015) Muscle degeneration is a prevalent disease, particularly in aging societies where it has a huge impact on quality of life and incurs colossal health costs. Suitable donor sources of smooth muscle cells are limited and minimally invasive therapeutic approaches... |
|
|
Electron paramagnetic resonance imaging for real-time monitoring of Li-ion batteries.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6276, (2015) Batteries for electrical storage are central to any future alternative energy paradigm. The ability to probe the redox mechanisms occurring at electrodes during their operation is essential to improve battery performances. Here we present the first report on ... |
|
|
Facile Synthesis of Coaxial CNTs/MnOx-Carbon Hybrid Nanofibers and Their Greatly Enhanced Lithium Storage Performance.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 17473, (2015) Carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/MnOx-Carbon hybrid nanofibers have been successfully synthesized by the combination of a liquid chemical redox reaction (LCRR) and a subsequent carbonization heat treatment. The nanostructures exhibit a unique one-dimensional core/shel... |
|
|
Direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and carbon dioxide over CeO2(X)-ZnO(1-X) nano-catalysts.
J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13(12) , 8116-20, (2013) CeO2(X)-ZnO(1-X) (X = 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, and 1.0) nano-catalysts were prepared by a co-precipitation method with a variation of CeO2 content (X, mol%), and they were applied to the direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and carbon dioxi... |
|
|
Comparative studies on exenatide-loaded poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles prepared by a novel ultra-fine particle processing system and spray drying.
Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 132 , 103-10, (2015) The purpose of this study was to compare the properties of exenatide-loaded poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles (Ex-PLGA-MPs) prepared by a novel ultra-fine particle processing system (UPPS) and spray drying. UPPS is a proprietary technology dev... |
|
|
High-capacity electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries: Li3NbO4-based system with cation-disordered rocksalt structure.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , 7650-5, (2015) Rechargeable lithium batteries have rapidly risen to prominence as fundamental devices for green and sustainable energy development. Lithium batteries are now used as power sources for electric vehicles. However, materials innovations are still needed to sati... |