| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisilazane
CAS:999-97-3 |
|
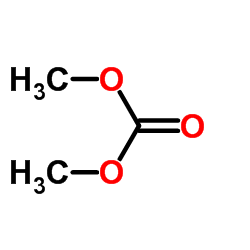 |
Dimethyl Carbonate
CAS:616-38-6 |
|
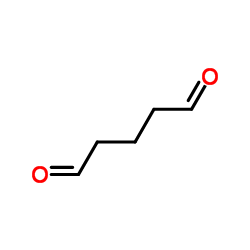 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
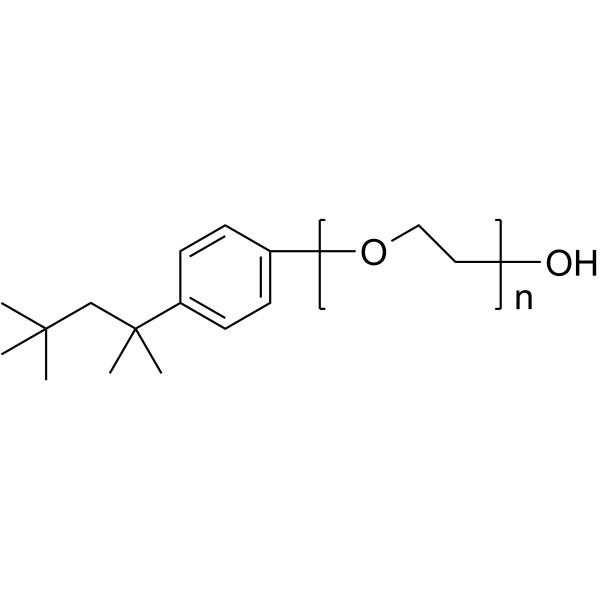 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
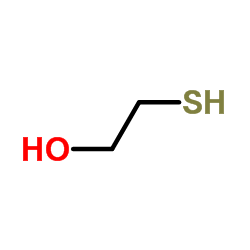 |
mercaptoethanol
CAS:60-24-2 |
|
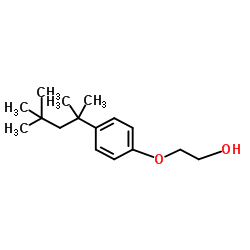 |
2-(4-(1,1,3,3-Tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy)ethanol
CAS:2315-67-5 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
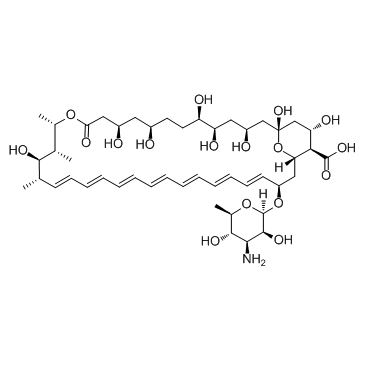 |
Amphotericin B
CAS:1397-89-3 |