bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane
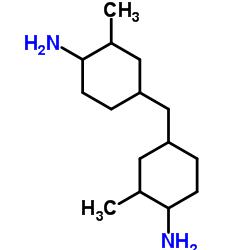
bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane structure
|
Common Name | bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6864-37-5 | Molecular Weight | 238.412 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 289.6±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H30N2 | Melting Point | -7°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 152.3±17.9 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Nephila clavipes spider dragline silk microstructure studied by scanning transmission X-ray microscopy.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(13) , 3897-905, (2007) Nephila clavipes dragline silk microstructure has been investigated by scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM), a technique that allows quantitative mapping of the level of orientation of the peptide groups at high spatial resolution (<50 nm). Maps of t... |
|
|
[Subacute toxicity of an amine-curing agent for epoxy resin].
Sangyo. Igaku. 26(3) , 197-204, (1984) Amine-curing agent for epoxy resin, bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane, has been suspected of inducing toxic symptoms in man which resemble collagen disease such as scleroderma or polymyositis. We studied subacute toxicity of this agent by repeated oral a... |
|
|
Clinico-pathological changes induced in rats treated with amine-curing agent for epoxy resin, bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane.
J. Toxicol. Sci. 11(2) , 79-93, (1986) Amine-curing agent for epoxy resin, bis(4-amino-3-methyl-cyclohexyl)methane (commercial name; Laromin C) has been suspected to have induced in the workers some toxic signs such as collagen disease like scleroderma or polymyositis. Subacute toxicity of this ag... |
|
|
[Scleroderma and scleroderma-like diseases caused by environmental pollutants].
Derm. Beruf Umwelt. 34(3) , 61-7, (1986) For the stimulation of research on scleroderma and the prophylaxis of occupational scleroderma-like diseases and the prevention of iatrogenic injuries, respect., it is important to know the inducing environmental substances. Plastics (vinyl chloride, epoxy re... |
|
|
Detection of sclerosis-inducing glycosaminoglycan in the skin of an amine-induced experimental skin sclerosis.
Dermatologica 161(3) , 145-51, (1980) The presence of sclerosis-inducing glycosaminoglycan in the skin was confirmed in an experimental skin sclerosis induced by a chemical compound. An experimental skin sclerosis was first produced in the mouse with bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane. Out of... |
|
|
Pathomorphological changes in rat brain choroid plexus due to administration of the amine-curing agent, bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane.
Virchows Arch. A. Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 417(3) , 203-12, (1990) Repeated oral administration of an amine-curing agent for epoxy resin, bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane, gave rise to severe damage in the choroid plexus of rat brain. The damaged epithelium presented varying degrees of swelling and hydropic vacuolation... |
|
|
Ultrastructural changes in rat Clara cells induced by bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane.
J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 28(2) , 249-55, (1989) Repeated oral administration of bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane to rats induced unusual ultrastructural changes in Clara cells of the bronchiolar epithelium, involving marked accumulation of electron-dense inclusion bodies with a lamellar structure in ... |
|
|
Fully aliphatic polyimides from adamantane-based diamines for enhanced thermal stability, solubility, transparency, and low dielectric constant. Mathews AS, et al.
J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102(4) , 3316-26, (2006)
|
|
|
Synthesis and characterization of novel fully aliphatic polyimidosiloxanes based on alicyclic or adamantyl diamines. Mathews AS, et al.
J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 44(18) , 5254-70, (2006)
|