Detection of sclerosis-inducing glycosaminoglycan in the skin of an amine-induced experimental skin sclerosis.
H Ishikawa, A Yamakage, M Kitabatake, H Katayama, Y Saito
Index: Dermatologica 161(3) , 145-51, (1980)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The presence of sclerosis-inducing glycosaminoglycan in the skin was confirmed in an experimental skin sclerosis induced by a chemical compound. An experimental skin sclerosis was first produced in the mouse with bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane. Out of glycosaminoglycans isolated from the slightly changed skin of this experimental skin sclerosis, the one having a heparan sulfate-like structure was able to again induce sclerotic skin changes in another mouse. The chemical composition of this sclerosis-inducing glycosaminoglycan was somewhat similar to that of the scleroderma-inducing glycosaminoglycan isolated previously from the urine of patients with systemic scleroderma.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
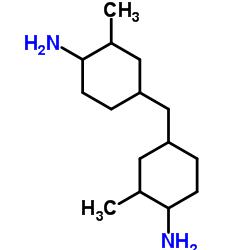 |
bis(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methane
CAS:6864-37-5 |
C15H30N2 |
|
Nephila clavipes spider dragline silk microstructure studied...
2007-04-04 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(13) , 3897-905, (2007)] |
|
[Subacute toxicity of an amine-curing agent for epoxy resin]...
1984-05-01 [Sangyo. Igaku. 26(3) , 197-204, (1984)] |
|
Clinico-pathological changes induced in rats treated with am...
1986-05-01 [J. Toxicol. Sci. 11(2) , 79-93, (1986)] |
|
[Scleroderma and scleroderma-like diseases caused by environ...
1986-01-01 [Derm. Beruf Umwelt. 34(3) , 61-7, (1986)] |
|
Pathomorphological changes in rat brain choroid plexus due t...
1990-01-01 [Virchows Arch. A. Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 417(3) , 203-12, (1990)] |