L(+)-Lysine monohydrate
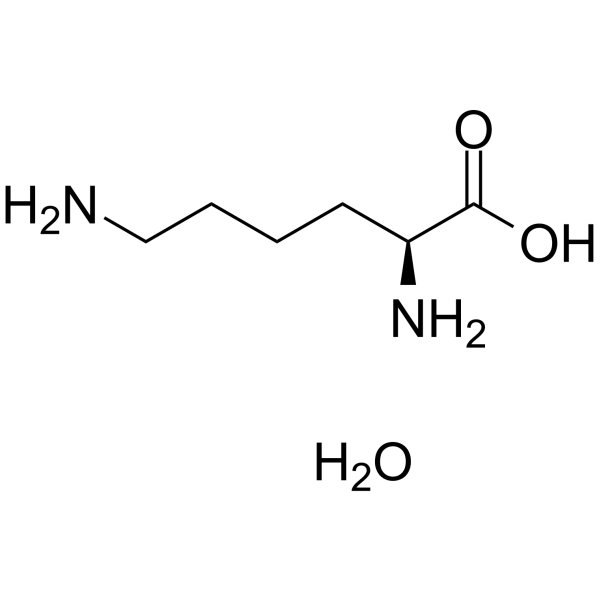
L(+)-Lysine monohydrate structure
|
Common Name | L(+)-Lysine monohydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39665-12-8 | Molecular Weight | 164.20300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 400ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H16N2O3 | Melting Point | 212-214 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 195.7ºC | |
|
Direct cellular delivery of human proteasomes to delay tau aggregation.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5633, (2014) The 26S proteasome is the primary machinery that degrades ubiquitin (Ub)-conjugated proteins, including many proteotoxic proteins implicated in neurodegeneraton. It has been suggested that the elevation of proteasomal activity is tolerable to cells and may be... |
|
|
A new antitumor enzyme, L-lysine alpha-oxidase from Trichoderma viride. Purification and enzymological properties.
J. Biol. Chem. 255 , 976, (1980) L-Lysine alpha-oxidase from Trichoderma viride Y244-2 has been purified to homogeneity. The enzyme shows absorption maxima at 277, 388, and 466 nm and a shoulder around 490 nm and contains 2 mol of FAD/mol of enzyme. The enzyme has a molecular weight of appro... |
|
|
Phosphoproteomic Profiling Reveals Epstein-Barr Virus Protein Kinase Integration of DNA Damage Response and Mitotic Signaling.
PLoS Pathog. 11(12) , e1005346, (2015) Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is etiologically linked to infectious mononucleosis and several human cancers. EBV encodes a conserved protein kinase BGLF4 that plays a key role in the viral life cycle. To provide new insight into the host proteins regulated by BGLF... |
|
|
Activity of α-Aminoadipate Reductase Depends on the N-Terminally Extending Domain.
ChemBioChem. 16(10) , 1426-30, (2015) L-α-Aminoadipic acid reductases catalyze the ATP- and NADPH-dependent reduction of L-α-aminoadipic acid to the corresponding 6-semialdehyde during fungal L-lysine biosynthesis. These reductases resemble peptide synthetases with regard to their multidomain com... |
|
|
Identification of inhibitors of chromatin modifying enzymes using the yeast phenotypic screens.
Methods Mol. Biol. 548 , 145-60, (2009) A multitude of enzymes that modify histones and remodel nucleosomes are required for the formation, maintenance, and propagation of the transcriptionally repressed chromatin state in eukaryotes. Robust phenotypic screens in yeast S. cerevisiae have proved ins... |
|
|
A practical recipe for stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC).
Nat. Protoc. 1(6) , 2650-60, (2006) Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) is a simple, robust, yet powerful approach in mass spectrometry (MS)-based quantitative proteomics. SILAC labels cellular proteomes through normal metabolic processes, incorporating non-radioactiv... |
|
|
Selenium is an essential trace nutrient for growth of WI-38 diploid human fibroblasts.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 73(6) , 2023-7, (1976) The trace element selenium is essential for clonal growth of diploid fibroblasts from human fetal lung (WI-38) in media containing small amounts of serum protein. Maximum growth stimulation is obtained when 30 nM neutralized selenious acid is added to a synth... |
|
|
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Maillard reaction products isolated from sugar-amino acid model systems.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 59 , 11294-11303, (2011) We investigated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of both crude and ultrafiltrated Maillard reaction (MR) products (MRPs) derived from sugar-amino acid MR models, comprising fructose (Fru), glucose (Glu) or ribose (Rib) reacted with glycine (Gl... |
|
|
Determination of advanced glycation endproducts by LC-MS/MS in raw and roasted almonds (Prunus dulcis).
J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(22) , 12037-46, (2011) A sensitive and reliable LC-(ESI)MS/MS method was developed and validated for the simultaneous analysis of five common advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) after enzymatic digestion in raw and roasted almonds. AGEs included carboxymethyl-lysine (CML), carbox... |
|
|
Moderate glycation of serum albumin affects folding, stability, and ligand binding.
Clin. Chim. Acta 412 , 2105-2116, (2011) Serum protein glycation and formation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGE) correlates with diabetic complications. Highly AGE-modified albumin is frequently used to study the biochemical and cellular activities of AGE-proteins. However, moderately modified... |