Nifedipine
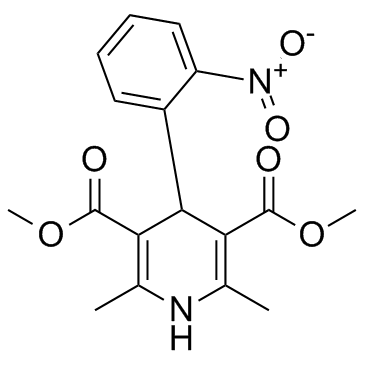
Nifedipine structure
|
Common Name | Nifedipine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21829-25-4 | Molecular Weight | 346.335 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 475.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18N2O6 | Melting Point | 171-175 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 241.2±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Ammonium increases Ca(2+) signalling and upregulates expression of Cav1.2 gene in astrocytes in primary cultures and in the in vivo brain.
Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 214 , 261-74, (2015) The primary aim of this study was to identify the effects of hyperammonaemia on functional expression of Cav1.2 L-type Ca(2+) channels in astroglia.Primary cultures of mouse astrocytes were used to study effects of chronic treatment (1-5 days) with ammonium c... |
|
|
A systemic evaluation of cardiac differentiation from mRNA reprogrammed human induced pluripotent stem cells.
PLoS ONE 9(7) , e103485, (2014) Genetically unmodified cardiomyocytes mandated for cardiac regenerative therapy is conceivable by "foot-print free" reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). In this study, we report generation of foot-print free hiPSC through m... |
|
|
Human lymphatic vessel contractile activity is inhibited in vitro but not in vivo by the calcium channel blocker nifedipine.
J. Physiol. 592(Pt 21) , 4697-714, (2014) Calcium channel blockers (CCB) are widely prescribed anti-hypertensive agents. The commonest side-effect, peripheral oedema, is attributed to a larger arterial than venous dilatation causing increased fluid filtration. Whether CCB treatment is detrimental to ... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental drug discovery projects toward safer medicines. In this st... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI types (hepatotoxic side effects) seen in the clinic can be tra... |
|
|
The Japanese toxicogenomics project: application of toxicogenomics.
Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 54 , 218-27, (2010) Biotechnology advances have provided novel methods for the risk assessment of chemicals. The application of microarray technologies to toxicology, known as toxicogenomics, is becoming an accepted approach for identifying chemicals with potential safety proble... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals can make a significant contribution to the identification o... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predictive in vivo, in vitro, and in silico models to identify comp... |
|
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Schisandrol B protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibition of CYP-mediated bioactivation and regulation of liver regeneration.
Toxicol. Sci. 143(1) , 107-15, (2014) Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose is the most frequent cause of drug-induced acute liver failure. Schisandra sphenanthera is a traditional hepato-protective Chinese medicine and Schisandrol B (SolB) is one of its major active constituents. In this study, the prot... |