Evans Blue
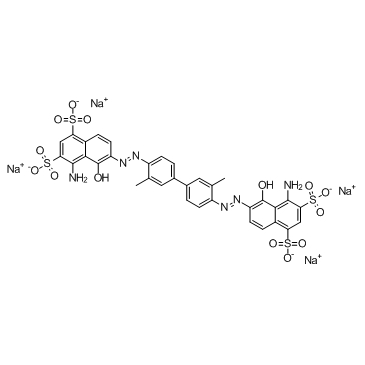
Evans Blue structure
|
Common Name | Evans Blue | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 314-13-6 | Molecular Weight | 960.805 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C34H24N6Na4O14S4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Targeting latent TGFβ release in muscular dystrophy.
Sci. Transl. Med. 6(259) , 259ra144, (2014) Latent transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) binding proteins (LTBPs) bind to inactive TGFβ in the extracellular matrix. In mice, muscular dystrophy symptoms are intensified by a genetic polymorphism that changes the hinge region of LTBP, leading to increased p... |
|
|
Emilin1 deficiency causes structural and functional defects of lymphatic vasculature.
Mol. Cell. Biol. 28(12) , 4026-39, (2008) Lymphatic-vasculature function critically depends on extracellular matrix (ECM) and on its connections with lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs). However, the composition and the architecture of ECM have not been fully taken into consideration in studying the b... |
|
|
Neurodegenerative evidence in mice brains with cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis: preventive effect of the free radical scavenger edaravone.
PLoS ONE 7(12) , e51539, (2012) Sepsis is a major clinical challenge and septic encephalopathy is its nasty complication. The pathogenesis and underlying mechanisms of septic encephalopathy are not well understood. This study sought to fully characterize sepsis-associated biochemical and hi... |
|
|
The involvement of potassium channels in the peripheral antiedematogenic effect of intrathecally injected morphine in rats.
Anesth. Analg. 116(1) , 232-8, (2013) A previous study indicated that intrathecal administration of morphine reduces experimental inflammatory edema in rats by activating the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway. This evidence supports the hypothesis that potassium channel opening ... |
|
|
TRPV1 channels control synaptic plasticity in the developing superior colliculus.
J. Physiol. 587(Pt 11) , 2521-35, (2009) Long-term depression (LTD) in the rodent superior colliculus (SC) is regarded as a model of synaptic refinement because it can be induced during development but not in adults. We investigated the role of transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 (TRPV1) c... |
|
|
The effect of an NK1 receptor antagonist on blood spinal cord barrier permeability following balloon compression-induced spinal cord injury.
Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 118 , 303-6, (2013) The blood spinal cord barrier (BSCB) is disrupted following spinal cord injury (SCI) resulting in vasogenic edema and increased intrathecal pressure (ITP). The neuropeptide substance P (SP) has been implicated in the development of blood-brain barrier (BBB) d... |
|
|
Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells to muscle fiber to model Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Nat. Biotechnol. , doi:10.1038/nbt.3297, (2015) During embryonic development, skeletal muscles arise from somites, which derive from the presomitic mesoderm (PSM). Using PSM development as a guide, we establish conditions for the differentiation of monolayer cultures of mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells into... |
|
|
The inhibitory effect of S-nitrosoglutathione on blood-brain barrier disruption and peroxynitrite formation in a rat model of experimental stroke.
J. Neurochem. 123 Suppl 2 , 86-97, (2012) The hallmark of stroke injury is endothelial dysfunction leading to blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage and edema. Among the causative factors of BBB disruption are accelerating peroxynitrite formation and the resultant decreased bioavailability of nitric oxide... |
|
|
Anti-angiogenic effect of KH902 on retinal neovascularization.
Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 251(9) , 2131-9, (2013) KH902 is a fusion protein derived from the extracellular domains of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors 1 and 2 and the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1). Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is an eye disease that affects premature babies wh... |
|
|
Blood-brain barrier transport of an essential amino acid after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury.
Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 118 , 297-302, (2013) Under pathophysiological conditions such as -cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (IR), damage to cerebrovascular endothelial cells causes alterations in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) function that can exacerbate neuronal cell injury and death. Clarifying changes in... |