L-threonolactone
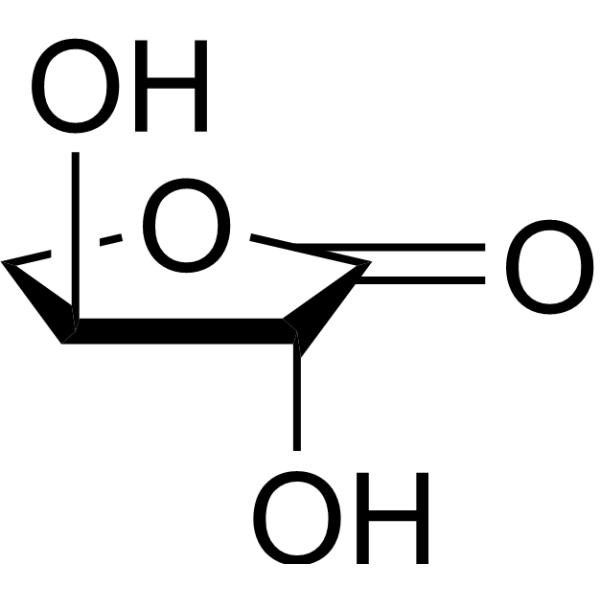
L-threonolactone structure
|
Common Name | L-threonolactone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21730-93-8 | Molecular Weight | 118.09 | |
| Density | 0.99g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 277.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 101.3ºC | |
|
A convenient preparation of aldonohydroxamic acids in water and crystal structure of L-erythronohydroxamic acid.
Carbohydr. Res. 335(3) , 195-204, (2001) Hydroxamic acids derived from aldonic acids, namely aldonohydroxamic acids, have become an increasingly important class of inhibitors of enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates. We now report the straightforward preparation of various types of ald... |
|
|
Alkaline and smith degradation of oxidized dermatan sulphate-chondroitin sulphate copolymers.
Carbohydr. Res. 36(2) , 349-58, (1974)
|
|
|
Metabolism of l-Threonic Acid in Rumex x acutus L. and Pelargonium crispum (L.) L'Hér.
Plant Physiol. 69(6) , 1365-8, (1982) l-Threonic acid is a natural constituent in leaves of Pelargonium crispum (L.) L'Hér (lemon geranium) and Rumex x acutus L. (sorrel). In both species, l-[(14)C]threonate is formed after feeding l-[U-(14)C]ascorbic acid to detached leaves. R. acutus leaves lab... |
|
|
Structural evidence for a 1,2-enediolate intermediate in the reaction catalyzed by 3-keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase, a member of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase suprafamily.
Biochemistry 42(42) , 12133-42, (2003) 3-Keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase (KGPDC) and orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC) are members of an enzyme suprafamily, the OMPDC suprafamily, because they are homologous enzymes that catalyze mechanistically distinct reactions using differ... |