L-threonolactone
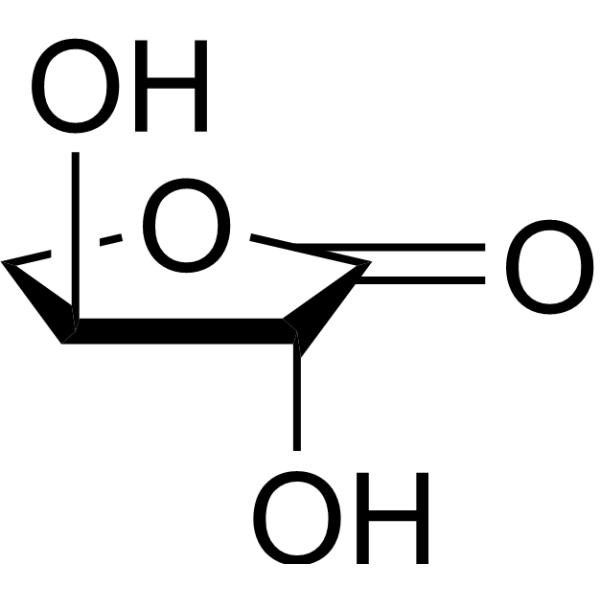
L-threonolactone structure
|
Common Name | L-threonolactone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21730-93-8 | Molecular Weight | 118.09 | |
| Density | 0.99g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 277.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 101.3ºC | |
Use of L-threonolactoneL-Threonolactone ((3R,4S)-3,4-Dihydroxyoxolan-2-one) is a purine nucleoside analog. Purine nucleoside analogs have broad antitumor activity targeting indolent lymphoid malignancies. Anticancer mechanisms in this process rely on inhibition of DNA synthesis, induction of apoptosis, etc[1]. |
| Name | L-threonolactone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Threonolactone ((3R,4S)-3,4-Dihydroxyoxolan-2-one) is a purine nucleoside analog. Purine nucleoside analogs have broad antitumor activity targeting indolent lymphoid malignancies. Anticancer mechanisms in this process rely on inhibition of DNA synthesis, induction of apoptosis, etc[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.99g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 277.8ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 118.09 |
| Flash Point | 101.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 118.02700 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.00443mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.437 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2932209090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| HS Code | 2932209090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932209090. other lactones. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
A convenient preparation of aldonohydroxamic acids in water and crystal structure of L-erythronohydroxamic acid.
Carbohydr. Res. 335(3) , 195-204, (2001) Hydroxamic acids derived from aldonic acids, namely aldonohydroxamic acids, have become an increasingly important class of inhibitors of enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates. We now rep... |
|
|
Alkaline and smith degradation of oxidized dermatan sulphate-chondroitin sulphate copolymers.
Carbohydr. Res. 36(2) , 349-58, (1974)
|
|
|
Metabolism of l-Threonic Acid in Rumex x acutus L. and Pelargonium crispum (L.) L'Hér.
Plant Physiol. 69(6) , 1365-8, (1982) l-Threonic acid is a natural constituent in leaves of Pelargonium crispum (L.) L'Hér (lemon geranium) and Rumex x acutus L. (sorrel). In both species, l-[(14)C]threonate is formed after feeding l-[U-(... |
| 2,3-dihydroxydihydrofuran-1-one |
| Threonolactone |
| di-TMS-Threono-1,4-lactone |
| (3R,4S)-3,4-Dihydroxydihydrofuran-2(3H)-one |
| L-threonic acid-4-lactone |
| threonic acid-1,4-lactone |
| L-treono-1,4-lactone |
| L-Threonic acid-1,4-lactone |
| (3R,4S)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-one |
| Bis-TMS-Threono-1,4-lactone |
| L-Threonsaeure-4-lacton |
| (3R,4S)-3,4-dihydroxy-dihydrofuran-2-one |
 CAS#:74421-65-1
CAS#:74421-65-1