1MVR
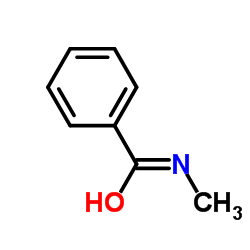
1MVR structure
|
Common Name | 1MVR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 613-93-4 | Molecular Weight | 135.163 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 254.9±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H9NO | Melting Point | 76-78 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 145.6±11.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Thermodynamic analysis of the binding of aromatic hydroxamic acid analogues to ferric horseradish peroxidase.
Biochemistry 40(46) , 13980-9, (2001) Peroxidases typically bind their reducing substrates weakly, with K(d) values in the millimolar range. The binding of benzhydroxamic acid (BHA) to ferric horseradish peroxidase isoenzyme C (HRPC) [K(d) = 2.4 microM; Schonbaum, G. R. (1973) J. Biol. Chem. 248,... |
|
|
N-Methylanilide and N-methylbenzamide derivatives as phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21(19) , 6053-62, (2013) PDE10A is a recently identified phosphodiesterase with a quite remarkable localization since the protein is abundant only in brain tissue. Based on this unique localization, research has focused extensively on using PDE10A modulators as a novel therapeutic ap... |
|
|
Molecular electrostatic potential of orthopramides: implications for their interaction with the D-2 dopamine receptor.
J. Med. Chem. 29(5) , 600-6, (1986) The electronic properties of orthopramides, a group of selective D-2 dopamine receptor antagonists, were investigated by calculating molecular electrostatic potentials (MEP) of model compounds with the ab initio STO-3G MO method. The various substitution patt... |
|
|
The formation and metabolism of N-hydroxymethyl compounds--III. The metabolic conversion of N-methyl and N,N,-dimethylbenzamides to N-hydroxymethyl compounds.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 32(11) , 1773-81, (1983) The stability of metabolically-generated N-(hydroxymethyl) compounds was investigated using a series of N-methylbenzamides as model substrates. N-(Hydroxymethyl)-benzamide was characterized as a major metabolite of N-methylbenzamide in vitro, and was also ide... |
|
|
The microsomal demethylation of N,N-dimethylbenzamides. Substituent and kinetic deuterium isotope effects.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 44(4) , 651-8, (1992) The metabolism of N,N-dimethylbenzamides by phenobarbital-induced rat liver microsomes results in the formation of N-methylbenzamides and formaldehyde. The reaction proceeds via the formation of an intermediate N-hydroxymethyl-N-methylbenzamide, which, for th... |
|
|
Discovery and in vitro and in vivo profiles of 4-fluoro-N-[4-[6-(isopropylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl]-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-N-methylbenzamide as novel class of an orally active metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) antagonist.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19(18) , 5464-8, (2009) We identified 4-fluoro-N-[4-[6-(isopropylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl]-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-N-methylbenzamide 27 as a potent mGluR1 antagonist. The compound possessed excellent subtype selectivity and good PK profile in rats. It also demonstrated relatively potent antip... |
|
|
Design and synthesis of substituted N-methylbenzamide analogues derived from SR 48,968 as neurokinin-2 receptor antagonists.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14(18) , 4779-82, (2004) A series of N-methylbenzamide analogues (2-18) that is structurally derived from SR 48,968, a potent neurokinin-2 (NK(2)) receptor antagonist (pK(b)9.1), has been obtained using asymmetric synthesis. Isothiocyanato-N-methylbenzamide (10-12) and bromoacetamido... |