EGTA
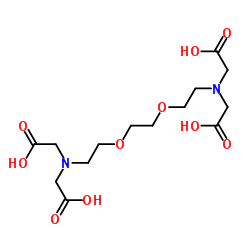
EGTA structure
|
Common Name | EGTA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67-42-5 | Molecular Weight | 380.348 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 678.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H24N2O10 | Melting Point | 241 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 363.9±31.5 °C | |
|
Functional consequence of the MET-T1010I polymorphism in breast cancer.
Oncotarget 6(5) , 2604-14, (2015) Major breast cancer predisposition genes, only account for approximately 30% of high-risk breast cancer families and only explain 15% of breast cancer familial relative risk. The HGF growth factor receptor MET is potentially functionally altered due to an unc... |
|
|
Immunomodulation by the Pseudomonas syringae HopZ type III effector family in Arabidopsis.
PLoS ONE 9(12) , e116152, (2014) Pseudomonas syringae employs a type III secretion system to inject 20-30 different type III effector (T3SE) proteins into plant host cells. A major role of T3SEs is to suppress plant immune responses and promote bacterial infection. The YopJ/HopZ acetyltransf... |
|
|
Targeting glucose uptake with siRNA-based nanomedicine for cancer therapy.
Biomaterials 51 , 1-11, (2015) Targeting cancer metabolism is emerging as a successful strategy for cancer therapy. However, most of the marketed anti-metabolism drugs in cancer therapy do not distinguish normal cells from cancer cells, leading to severe side effects. In this study, we rep... |
|
|
Effect of (2)H and (18)O water isotopes in kinesin-1 gliding assay.
PeerJ 2 , e284, (2014) We show for the first time the effects of heavy-hydrogen water ((2)H2O) and heavy-oxygen water (H2 (18)O) on the gliding speed of microtubules on kinesin-1 coated surfaces. Increased fractions of isotopic waters used in the motility solution decreased the gli... |
|
|
Calcium-induced conformational changes of the regulatory domain of human mitochondrial aspartate/glutamate carriers.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5491, (2014) The transport activity of human mitochondrial aspartate/glutamate carriers is central to the malate-aspartate shuttle, urea cycle, gluconeogenesis and myelin synthesis. They have a unique three-domain structure, comprising a calcium-regulated N-terminal domai... |
|
|
DOCK2 and DOCK5 act additively in neutrophils to regulate chemotaxis, superoxide production, and extracellular trap formation.
J. Immunol. 193(11) , 5660-7, (2014) Neutrophils are highly motile leukocytes that play important roles in the innate immune response to invading pathogens. Neutrophils rapidly migrate to the site of infections and kill pathogens by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS). Neutrophil chemotaxis ... |
|
|
Calcitonin controls bone formation by inhibiting the release of sphingosine 1-phosphate from osteoclasts.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 5215, (2014) The hormone calcitonin (CT) is primarily known for its pharmacologic action as an inhibitor of bone resorption, yet CT-deficient mice display increased bone formation. These findings raised the question about the underlying cellular and molecular mechanism of... |
|
|
Functional screening in Drosophila reveals the conserved role of REEP1 in promoting stress resistance and preventing the formation of Tau aggregates.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 23(25) , 6762-72, (2014) Pathological modifications in the microtubule-associated protein Tau is a common characteristic observed in different neurological diseases, suggesting that analogous metabolic pathways might be similarly affected during neurodegeneration. To identify these m... |
|
|
The protein phosphatase Siw14 controls caffeine-induced nuclear localization and phosphorylation of Gln3 via the type 2A protein phosphatases Pph21 and Pph22 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
J. Biochem. 157(1) , 53-64, (2015) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Siw14, a tyrosine phosphatase involved in the response to caffeine, participates in regulation of the phosphorylation and intracellular localization of Gln3, a GATA transcriptional activator of nitrogen catabolite repression-sensi... |
|
|
Novel in silico-designed estradiol analogues are cytotoxic to a multidrug-resistant cell line at nanomolar concentrations.
Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 75(2) , 431-7, (2015) 2-Methoxyestradiol (2ME) is a promising anti-cancer agent that disrupts the integrity and dynamics of the spindle network. In order to overcome the pharmacokinetic constraints of this compound, a panel of sulphamoylated estradiol analogues were in silico-desi... |