Amitrole
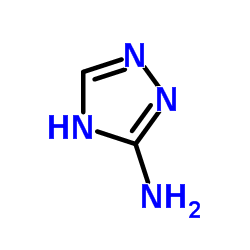
Amitrole structure
|
Common Name | Amitrole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 61-82-5 | Molecular Weight | 84.080 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 85.4±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H4N4 | Melting Point | 150-153 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 5.4±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
S-nitrosylation triggers ABI5 degradation to promote seed germination and seedling growth.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 8669, (2015) Plant survival depends on seed germination and progression through post-germinative developmental checkpoints. These processes are controlled by the stress phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA). ABA regulates the basic leucine zipper transcriptional factor ABI5, a... |
|
|
Quantitative structure-activity relationship and complex network approach to monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors.
J. Med. Chem. 51 , 6740-51, (2008) The work provides a new model for the prediction of the MAO-A and -B inhibitor activity by the use of combined complex networks and QSAR methodologies. On the basis of the obtained model, we prepared and assayed 33 coumarin derivatives, and the theoretical pr... |
|
|
Direct and indirect inactivation of tumor cell protective catalase by salicylic acid and anthocyanidins reactivates intercellular ROS signaling and allows for synergistic effects.
Carcinogenesis 36(3) , 400-11, (2015) Salicylic acid and anthocyanidins are known as plant-derived antioxidants, but also can provoke paradoxically seeming prooxidant effects in vitro. These prooxidant effects are connected to the potential of salicylic acid and anthocyanidins to induce apoptosis... |
|
|
Allosteric ligands for the pharmacologically dark receptors GPR68 and GPR65.
Nature 527(7579) , 477-83, (2015) At least 120 non-olfactory G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome are 'orphans' for which endogenous ligands are unknown, and many have no selective ligands, hindering the determination of their biological functions and clinical relevance. Among thes... |
|
|
FERONIA receptor kinase interacts with S-adenosylmethionine synthetase and suppresses S-adenosylmethionine production and ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.
Plant Cell Environ. 38 , 2566-74, (2015) Environmental inputs such as stress can modulate plant cell metabolism, but the detailed mechanism remains unclear. We report here that FERONIA (FER), a plasma membrane receptor-like kinase, may negatively regulate the S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) synthesis by ... |
|
|
Inhibitors of hydroperoxide metabolism enhance ascorbate-induced cytotoxicity.
Free Radic. Res. 47(3) , 154-63, (2013) Pharmacological ascorbate, via its oxidation, has been proposed as a pro-drug for the delivery of H(2)O(2) to tumors. Pharmacological ascorbate decreases clonogenic survival of pancreatic cancer cells, which can be reversed by treatment with scavengers of H(2... |
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum XPD translocates in 5' to 3' direction, is expressed throughout the blood stages, and interacts with p44.
Protoplasma 252 , 1487-504, (2015) XPD helicase, a TFIIH subunit, is essential for several processes including transcription, NER, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis in eukaryotes. Another component of TFIIH, namely p44, is among the well-known interacting partners of XPD and is vital in reg... |
|
|
A factor converting viable but nonculturable Vibrio cholerae to a culturable state in eukaryotic cells is a human catalase.
Microbiologyopen 4 , 589-96, (2015) In our previous work, we demonstrated that viable but nonculturable (VBNC) Vibrio cholerae O1 and O139 were converted to culturable by coculture with eukaryotic cells. Furthermore, we isolated a factor converting VBNC V. cholerae to culturable (FCVC) from a e... |
|
|
Novel bioassay for the discovery of inhibitors of the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) and terpenoid pathways leading to carotenoid biosynthesis.
PLoS ONE 9(7) , e103704, (2014) The 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway leads to the synthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate in plastids. It is a major branch point providing precursors for the synthesis of carotenoids, tocopherols, plastoquinone and the phytyl chain of chlorophy... |
|
|
Hydrogen Peroxide Induce Human Cytomegalovirus Replication through the Activation of p38-MAPK Signaling Pathway.
Viruses 7 , 2816-33, (2015) Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a major risk factor in transplantation and AIDS patients, which induces high morbidity and mortality. These patients infected with HCMV experience an imbalance of redox homeostasis that cause accumulation of reactive oxygen spe... |