Methacrylic anhydride
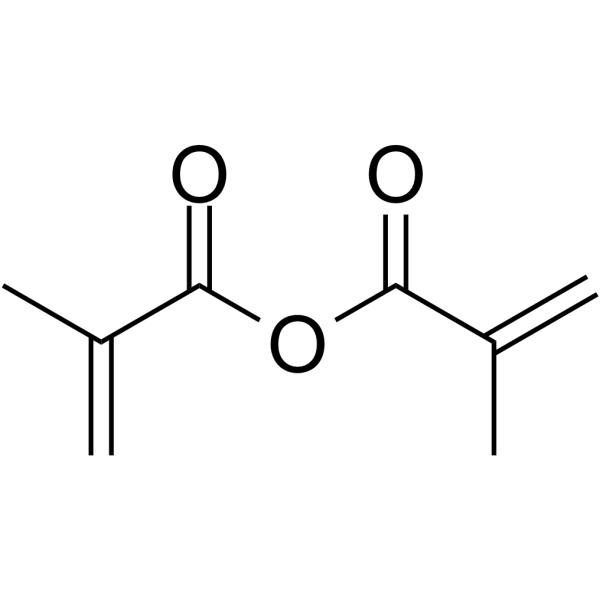
Methacrylic anhydride structure
|
Common Name | Methacrylic anhydride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 760-93-0 | Molecular Weight | 154.163 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 202.3±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O3 | Melting Point | -20°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 84.4±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Injectable Peptide Decorated Functional Nanofibrous Hollow Microspheres to Direct Stem Cell Differentiation and Tissue Regeneration.
Adv. Funct. Mater. 25(3) , 350-360, (2015) Injectable microspheres are attractive stem cell carriers for minimally invasive procedures. For tissue regeneration, the microspheres need to present the critical cues to properly direct stem cell differentiation. In natural extracellular matrix (ECM), growt... |
|
|
Enhanced chondrogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells using nanopatterned PEG-GelMA-HA hydrogels.
Tissue Eng. Part A 20(21-22) , 2817-29, (2014) We have examined the effects of surface nanotopography and hyaluronic acid (HA) on in vitro chondrogenesis of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). Ultraviolet-assisted capillary force lithography was employed to fabricate well-defined nanostructured scaffolds of c... |
|
|
Chondroitin sulfate-polyethylenimine copolymer-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as an efficient magneto-gene carrier for microRNA-encoding plasmid DNA delivery.
Nanoscale 7 , 8554-65, (2015) MicroRNA-128 (miR-128) is an attractive therapeutic molecule with powerful glioblastoma regulation properties. However, miR-128 lacks biological stability and leads to poor delivery efficacy in clinical applications. In our previous study, we demonstrated two... |
|
|
Quercetin-imprinted chromatographic sorbents revisited: optimization of synthesis and rebinding protocols for application to natural resources.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1364 , 128-39, (2014) Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) based on quercetin and synthesized by either bulk, precipitation or suspension polymerization were characterized in terms of size and shape by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).... |
|
|
Stiffening hydrogels for investigating the dynamics of hepatic stellate cell mechanotransduction during myofibroblast activation.
Sci. Rep. 6 , 21387, (2016) Tissue fibrosis contributes to nearly half of all deaths in the developed world and is characterized by progressive matrix stiffening. Despite this, nearly all in vitro disease models are mechanically static. Here, we used visible light-mediated stiffening hy... |
|
|
The use of covalently immobilized stem cell factor to selectively affect hematopoietic stem cell activity within a gelatin hydrogel.
Biomaterials 67 , 297-307, (2015) Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are a rare stem cell population found primarily in the bone marrow and responsible for the production of the body's full complement of blood and immune cells. Used clinically to treat a range of hematopoietic disorders, there i... |
|
|
Hyaluronic acid enhances the mechanical properties of tissue-engineered cartilage constructs.
PLoS ONE 9(12) , e113216, (2014) There is a need for materials that are well suited for cartilage tissue engineering. Hydrogels have emerged as promising biomaterials for cartilage repair, since, like cartilage, they have high water content, and they allow cells to be encapsulated within the... |
|
|
Injectable and photocross-linkable gels based on gellan gum methacrylate: a new tool for biomedical application.
Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 72 , 1335-42, (2014) In this work, a natural polysaccharide gellan gum (GG) has been modified with methacrylic groups (GG-MA) and combined with polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEG-DMA) in order to create novel injectable hydrogels that can be easily delivered through a needle... |
|
|
Directing valvular interstitial cell myofibroblast-like differentiation in a hybrid hydrogel platform.
Adv. Healthc. Mater. 4(1) , 121-30, (2015) Three dimensional (3D) hydrogel platforms are powerful tools, providing controllable, physiologically relevant microenvironments that could aid in understanding how various environmental factors direct valvular interstitial cell (VIC) phenotype. Continuous ac... |
|
|
Mechanical loading regulates human MSC differentiation in a multi-layer hydrogel for osteochondral tissue engineering.
Acta Biomater. 21 , 142-53, (2015) A bioinspired multi-layer hydrogel was developed for the encapsulation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) as a platform for osteochondral tissue engineering. The spatial presentation of biochemical cues, via incorporation of extracellular matrix analogs,... |