Triparanol
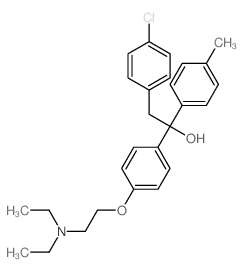
Triparanol structure
|
Common Name | Triparanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 78-41-1 | Molecular Weight | 438.00100 | |
| Density | 1.133g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 546.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32ClNO2 | Melting Point | 102.9-103.7ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 284.5ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Transcriptional Regulation of Cytosolic Sulfotransferase 1C2 by Intermediates of the Cholesterol Biosynthetic Pathway in Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 355 , 429-41, (2015) Cytosolic sulfotransferase 1C2 (SULT1C2) is expressed in the kidney, stomach, and liver of rats; however, the mechanisms regulating expression of this enzyme are not known. We evaluated transcriptional regulation of SULT1C2 by mevalonate (MVA)-derived interme... |
|
|
Teratogen-mediated inhibition of target tissue response to Shh signaling.
Science 280(5369) , 1603-7, (1998) Veratrum alkaloids and distal inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis have been studied for more than 30 years as potent teratogens capable of inducing cyclopia and other birth defects. Here, it is shown that these compounds specifically block the Sonic hedgeh... |
|
|
Triggering of Erythrocyte Death by Triparanol.
Toxins (Basel.) 7 , 3359-71, (2015) The cholesterol synthesis inhibitor Triparanol has been shown to trigger apoptosis in several malignancies. Similar to the apoptosis of nucleated cells, erythrocytes may enter eryptosis, the suicidal death characterized by cell shrinkage and cell membrane scr... |
|
|
Hypercholesterolemia: new findings and clinical applications. Introduction.
Am. J. Med. 91(1B) , 1S-2S, (1991)
|
|
|
Newborn response to cationic amphiphilic drugs.
Fed. Proc. 44(7) , 2323-7, (1985) Administration of various cationic amphiphilic drugs in utero results in induction of a phospholipid storage disorder in many tissues, particularly in lungs. In addition to the phospholipidosis in utero, drug exposure results in toxicity to the offspring; new... |
|
|
The effects of drugs and chemicals upon the structure of the adrenal gland.
Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 4(1) , 105-19, (1984) The susceptibility of the endocrine tissues to compound-induced lesions may be ranked in the following decreasing order of frequency: adrenal, testis, thyroid, ovary, pancreas, pituitary, and parathyroid. The first two are by far the most frequently affected.... |
|
|
Role of cholesterol in embryonic development.
Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71(5 Suppl) , 1270S-9S, (2000) We showed previously that 3 distal inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis are highly teratogenic in rats. AY 9944 and BM 15766 inhibit 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase, which catalyzes the last step of cholesterol synthesis, and triparanol inhibits Delta(24)-dehyd... |
|
|
Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. Effects of inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis on enzyme activity.
Biochem. J. 241(2) , 345-51, (1987) Incubating Hep G2 cells for 18 h with triparanol, buthiobate and low concentrations (less than 0.5 microM) of U18666A, inhibitors of desmosterol delta 24-reductase, of lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase and of squalene-2,3-epoxide cyclase (EC 5.4.99.7) respectiv... |
|
|
Polyterpenoids as cholesterol and tetrahymanol surrogates in the ciliate Tetrahymena pyriformis.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 960(2) , 190-9, (1988) The tetracyclic sterol precursors, cyclolaudenol, cycloartenol and lanosterol, inhibit efficiently the tetrahymanol biosynthesis in the ciliate Tetrahymena pyriformis, as reported earlier for cholesterol and other sterols. The prokaryotic bacteriohopanetetrol... |
|
|
Fatty acid metabolism in Paramecium. Oleic acid metabolism and inhibition of polyunsaturated fatty acid synthesis by triparanol.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 795(1) , 20-9, (1984) Paramecium requires oleic acid for growth and can grow in media containing no other fatty acids. In the present study, we have shown that this ciliate utilized oleate mainly as a carbon and energy source, even though this fatty acid was the only substrate ava... |