(-)-Indolactam V
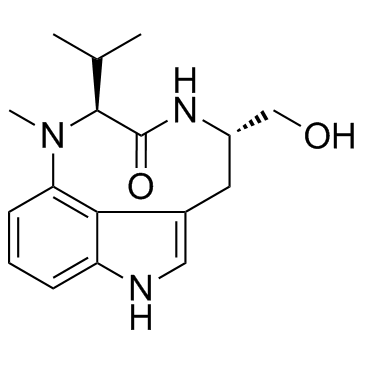
(-)-Indolactam V structure
|
Common Name | (-)-Indolactam V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 90365-57-4 | Molecular Weight | 301.383 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 584.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H23N3O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 307.0±30.1 °C | |
|
Structural basis of RasGRP binding to high-affinity PKC ligands.
J. Med. Chem. 45(4) , 853-60, (2002) The Ras guanyl releasing protein RasGRP belongs to the CDC25 class of guanyl nucleotide exchange factors that regulate Ras-related GTPases. These GTPases serve as switches for the propagation and divergence of signaling pathways. One interesting feature of Ra... |
|
|
Tumor promoter binding of the protein kinase C C1 homology domain peptides of RasGRPs, chimaerins, and Unc13s.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12(17) , 4575-83, (2004) Recent investigations discovered nonkinase-type phorbol ester receptors, RasGRPs, chimaerins, and Unc13s. Phorbol ester binding occurs at the cysteine-rich sequences of about 50 residues in the C1 domains of these receptors. Fifty-one-residue RasGRP C1 peptid... |
|
|
Indolactam and benzolactam compounds as new medicinal leads with binding selectivity for C1 domains of protein kinase C isozymes.
Curr. Pharm. Des. 10(12) , 1371-85, (2004) Protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes (alpha, betaI, betaII, gamma, delta, epsilon, eta, theta) are major receptors of tumor promoters and also play a crucial role in cellular signal transduction via the second messenger, 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol (DG). Each isozyme o... |
|
|
Binding selectivity of conformationally restricted analogues of (-)-indolactam-V to the C1 domains of protein kinase C isozymes.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 66(7) , 1615-7, (2002) Two conformationally restricted analogues of (-)-indolactam-V (1) (cis and trans amides) were examined for their binding selectivity to the synthetic C1 peptides of all protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes. Although the binding constants of the cis amide-restricte... |
|
|
Protein kinase signalling requirements for metabotropic action of kainate receptors in rat CA1 pyramidal neurones.
J. Physiol. 579(Pt 2) , 363-73, (2007) Hippocampal pyramidal neurones display a Ca(2+)-dependent K(+) current responsible for the slow afterhyperpolarization (I(sAHP)), a prominent regulator of excitability. There is considerable transmitter convergence onto I(sAHP) but little information about th... |
|
|
Identification of protein kinase C activation as a novel mechanism for RGS2 protein upregulation through phenotypic screening of natural product extracts.
Mol. Pharmacol. 86(4) , 406-16, (2014) Biochemical high-throughput screening is widely used in drug discovery, using a variety of small molecule libraries. However, broader screening strategies may be more beneficial to identify novel biologic mechanisms. In the current study we used a β-galactosi... |
|
|
PKC signalling regulates tight junction membrane assembly in the pre-implantation mouse embryo.
Reproduction 127(6) , 653-67, (2004) Epithelial differentiation including tight junction (TJ) formation occurs exclusively within the trophectoderm (TE) lineage of the mouse blastocyst. Here we examine mechanisms by which TJ protein membrane assembly might be regulated by protein kinase C (PKC) ... |
|
|
Protein kinase C-induced disorganization and endocytosis of photosensitive membrane in Limulus ventral photoreceptors.
J. Comp. Neurol. 442(3) , 217-25, (2002) Protein kinase C (PKC) desensitizes the light response in photoreceptors from the ventral optic nerve of the horseshoe crab Limulus. Photoisomerization of Limulus rhodopsin leads to phosphoinositide hydrolysis, resulting in the production of inositol trisphos... |
|
|
Effect of histamine on phasic and tonic contractions of isolated uterine tissue from pregnant women.
Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 188(3) , 774-8, (2003) To enhance our understanding of the uterotonic effect of histamine, we compared the effects of histamine on spontaneous phasic and tonic contractile activity of uterine strips from term pregnant nonlaboring women.Longitudinal uterine strips were used from the... |
|
|
Morphine inhibits indolactam V-induced U937 cell adhesion and gelatinase secretion.
J. Cell Physiol. 189(2) , 179-88, (2001) We demonstrate that indolactam V, a non-phorbol protein kinase C activator, promotes U937 cell attachment to fibronectin, type IV collagen and laminin. In the absence of indolactam V, 2-4% of U937 cells attach to all test substrates, however, in the presence ... |