H-7
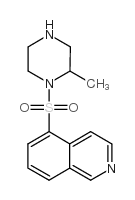
H-7 structure
|
Common Name | H-7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 84477-87-2 | Molecular Weight | 291.36900 | |
| Density | 1.277 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 495.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H17N3O2S | Melting Point | 114 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 253.3ºC | |
|
Protein kinase A stimulates Kv7.1 surface expression by regulating Nedd4-2-dependent endocytic trafficking.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 309 , C693-706, (2015) The potassium channel Kv7.1 plays critical physiological roles in both heart and epithelial tissues. In heart, Kv7.1 and the accessory subunit KCNE1 forms the slowly activating delayed-rectifier potassium current current, which is enhanced by protein kinase A... |
|
|
Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil in the striatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesion mouse model of Parkinson disease.
J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 73(8) , 770-9, (2014) Chronic degeneration of nigrostriatal projections, followed by nigral dopaminergic cell death, is a key feature of Parkinson disease (PD). This study examines the neuroprotective potential of the rho kinase inhibitor fasudil in the 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) ... |
|
|
Co-receptors are dispensable for tethering receptor-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells.
Cell Death Dis. 6 , e1772, (2015) During efferocytosis, phagocytic cells recognize dying cells by receptors binding to ligands specifically exposed on apoptotic cells. Multiple phagocytic receptors and some of their signaling pathways have been identified. However, the downstream pathways of ... |
|
|
Che-1-induced inhibition of mTOR pathway enables stress-induced autophagy.
EMBO J. 34 , 1214-30, (2015) Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a key protein kinase that regulates cell growth, metabolism, and autophagy to maintain cellular homeostasis. Its activity is inhibited by adverse conditions, including nutrient limitation, hypoxia, and DNA damage. In th... |
|
|
Widdrol-induced lipolysis is mediated by PKC and MEK/ERK in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Mol. Cell Biochem. 410 , 247-54, (2015) Obesity is a serious medical condition causing various diseases such as heart disease, type-2 diabetes, and cancer. Fat cells (adipocytes) play an important role in the generation of energy through hydrolysis of lipids they accumulate. Therefore, induction of... |
|
|
Multidirectional effects of calmodulin kinase II on transmitter release in mature and newly formed mouse motor synapses.
Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 154(3) , 316-9, (2013) Calmodulin inhibitor W-7 did not cause changes in the quantal content of postsynaptic end-plate potentials (EPP) in newly formed synapses, but prevented facilitation of acetylcholine secretion induced by L-type Ca(2+)channels blocker nitrendipine. CaMKII inhi... |
|
|
The selective Rho-kinase inhibitor azaindole-1 has long-lasting erectile activity in the rat.
Urology 81(2) , 465.e7-14, (2013) To investigate the effects of the selective Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor azaindole-1 on erectile function under physiologic and pathophysiologic conditions in the rat.The effect of intracavernosal (i.c.) injections of azaindole-1 on change i... |
|
|
Prevention of posterior capsular opacification.
Exp. Eye Res. 136 , 100-15, (2015) Posterior capsular opacification (PCO) is a common complication of cataract surgery. The development of PCO is due to a combination of the processes of proliferation, migration, and transdifferentiation of residual lens epithelial cells (LECs) on the lens cap... |
|
|
Central Rho kinase inhibition restores baroreflex sensitivity and angiotensin II type 1 receptor protein imbalance in conscious rabbits with chronic heart failure.
Hypertension 61(3) , 723-9, (2013) The small GTPase RhoA and its associated kinase ROCKII are involved in vascular smooth muscle cell contraction and endothelial NO synthase mRNA destabilization. Overactivation of the RhoA/ROCKII pathway is implicated in several pathologies, including chronic ... |
|
|
Cell migration towards CXCL12 in leukemic cells compared to breast cancer cells.
Cell. Signal. 28 , 316-24, (2016) Chemotaxis or directed cell migration is mediated by signalling events initiated by binding of chemokines to their cognate receptors and the activation of a complex signalling cascade. The molecular signalling pathways involved in cell migration are important... |