BOP reagent
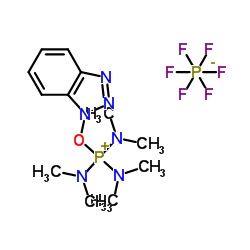
BOP reagent structure
|
Common Name | BOP reagent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56602-33-6 | Molecular Weight | 442.28 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H22F6N6OP2 | Melting Point | >130 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 138°C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Protease-degradable electrospun fibrous hydrogels.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6639, (2015) Electrospun nanofibres are promising in biomedical applications to replicate features of the natural extracellular matrix (ECM). However, nearly all electrospun scaffolds are either non-degradable or degrade hydrolytically, whereas natural ECM degrades proteo... |
|
|
Supramolecular hydrogels for long-term bioengineered stem cell therapy.
Adv. Healthc. Mater. 4(2) , 237-44, (2015) Synthetic hydrogels have been extensively investigated as artificial extracellular matrices (ECMs) for tissue engineering in vitro and in vivo. Crucial challenges for such hydrogels are sustaining long-term cytocompatible encapsulation and providing appropria... |
|
|
Synthesis and characterization of a new Peptide prodrug of glucosamine with enhanced gut permeability.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0126786, (2015) The aim of this study was to synthesize a peptide prodrug of glucosamine (GlcN) with increased gut permeability through the gut peptide transporter 1 (PepT1). Glycine-Valine ester derivative of GlcN (GVG) was synthesised using solid phase synthesis followed b... |
|
|
The effect of conventional mechanical periodontal treatment on red complex microorganisms and clinical parameters in Down syndrome periodontitis patients: a pilot study.
Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 34(3) , 601-8, (2015) Periodontal disease (PD) is induced by a complex microbiota, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, and Treponema denticola (together called the red complex), which triggers intense inflammatory reaction. Down syndrome (DS) individuals demons... |
|
|
Biphasic Alterations in Expression and Subcellular Localization of MUC1 in Pancreatic Ductal Carcinogenesis in Syrian Hamsters.
Pancreas 44(1) , 76-86, (2014) The aim of the present study was to characterize molecular targets for the prevention/diagnosis of pancreatic cancer using a chemically induced hamster pancreatic carcinogenesis model, in which background injuries to the parenchyma, for example, chronic pancr... |
|
|
Clinical outcome of double crown-retained implant overdentures with zirconia primary crowns.
J. Adv. Prosthodont. 7 , 329-37, (2015) This retrospective study aims at the evaluation of implant-supported overdentures (IODs) supported by ceramo-galvanic double crowns (CGDCs: zirconia primary crowns + galvano-formed secondary crown).In a private practice, 14 patients were restored with 18 IODs... |
|
|
Antigenicity studies in humans and immunogenicity studies in mice: an MSP1P subdomain as a candidate for malaria vaccine development.
Microbes Infect. 16(5) , 419-28, (2014) The newly identified GPI-anchored Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 1 paralog (MSP1P) has a highly antigenic C-terminus that binds erythrocytes. To characterize the antigenicity and immunogenicity of two regions (PvMSP1P-19 and -33) of the highly con... |
|
|
Surface characterization and drug release from porous microparticles based on methacrylic monomers and xanthan.
Carbohydr. Polym. 125 , 323-33, (2015) Porous crosslinked microparticles based on glycidyl methacrylate and xanthan were prepared by suspension polymerization and used for loading theophylline, a bronhodilatator drug, in order to obtain new drug delivery systems. The surface morphologies observed ... |
|
|
Synergistic Effects of SDF-1α and BMP-2 Delivery from Proteolytically Degradable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Bone Repair.
Macromol. Biosci. 15 , 1218-23, (2015) In order to achieve bone repair, bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) is typically delivered in non-physiological doses and can result in significant adverse side effects. To reduce the amount of BMP-2 necessary for bone formation, we delivered a known chemok... |
|
|
Influence of solid support, solvent and coupling reagent on the head-to-tail cyclization of resin-bound peptides.
Pept. Res. 7(4) , 195-206, (1994) Head-to-tail cyclization of peptides attached to insoluble supports by means of the side chains of aspartic acid or glutamic acid allows the rapid synthesis of cyclic peptides of widely varied amino acid sequence. However, two side reactions dramatically redu... |