Diafenthiuron
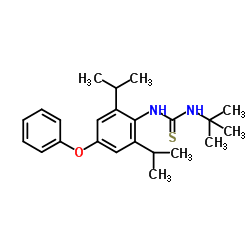
Diafenthiuron structure
|
Common Name | Diafenthiuron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 80060-09-9 | Molecular Weight | 384.578 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 448.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H32N2OS | Melting Point | 144.6-147.7°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 225.2±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Multi-residue method for determination of 238 pesticides in Chinese cabbage and cucumber by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: comparison of different purification procedures.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(47) , 11449-56, (2014) This paper describes the comparison of five sample cleanup procedures for the determination of 238 pesticides via triple quadrupole liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS, with only 10 min of chromatographic running time) in Chinese cabbage ... |
|
|
Diafenthiuron residue and decline in pakchoi and soil under field application.
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 79 , 75-9, (2012) A simple analytical method based on QuEChERs was established for diafenthiuron residues in packhoi and soil. The residue levels and diaaipation rates of diafenthiuron in packhoi and soil were detected by HPLC-MS. And ultrasonic extraction was employed in the ... |
|
|
Field efficacy and baseline toxicities of pyriproxifen, acetamiprid, and diafenthiuron against Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) in Burkina Faso (West Africa).
J. Environ. Sci. Health B 38(6) , 757-69, (2003) Bioassays were conducted in 2001 and 2002 to estimate toxicities and dose-response relationships of 24 Bemisica tabaci Gennadius populations to pyriproxifen, acemitaprid, and diafenthiuron. LC50s ranging from 0.014 to 0.096 mgL(-1), 0.60 to 1.3 mgL(-1), and 3... |
|
|
Toxicity of diafenthiuron to honey bees in laboratory, semi-field and field conditions.
Pest Manag. Sci. 66(5) , 505-10, (2010) Cardamom, an important spice crop often attacked by many insect pests, is controlled mainly using synthetic insecticides. As honey bees play a vital role in pollination in cardamom, the impact of insecticides on honey bees needs to be explored to assess its s... |
|
|
Photodegradation of diafenthiuron in water.
Pest Manag. Sci. 58(5) , 496-502, (2002) Diafenthiuron, 1-tert-butyl-3-(2,6-di-isopropyl-4-phenoxyphenyl)thiourea, is an effective insecticide and acaricide. Sunlight degradation of diafenthiuron in various aqueous solutions and pure hexane yielded two major identified products: 1-tert-butyl-3-(2,6-... |
|
|
Metabolism of diafenthiuron by microsomal oxidation: procide activation and inactivation as mechanisms contributing to selectivity.
Pest Manag. Sci. 57(10) , 975-80, (2001) The thiourea insecticide/acaricide diafenthiuron represents a biologically inactive propesticide that requires transformation into the active carbodiimide derivative. The carbodiimide inhibits mitochondrial respiration by selective and covalent binding to the... |
|
|
The thiourea insecticide diafenthiuron inhibits mitochondrial ATPase in vitro and in vivo by its carbodiimide product.
Biochem. Soc. Trans. 22(1) , 241-4, (1994)
|
|
|
Dissipation of foliar residues of diafenthiuron and its metabolites.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 68(6) , 845-51, (2002)
|