Propanil
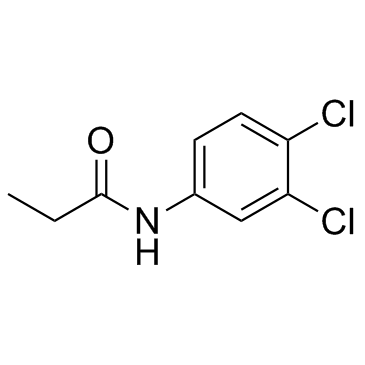
Propanil structure
|
Common Name | Propanil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 709-98-8 | Molecular Weight | 218.08000 | |
| Density | 1.25 | Boiling Point | 369.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H9Cl2NO | Melting Point | 92-93°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Temporal endogenous gene expression profiles in response to polymer-mediated transfection and profile comparison to lipid-mediated transfection.
J. Gene Med. 17(1-2) , 33-53, (2015) Design of efficient nonviral gene delivery systems is limited by the rudimentary understanding of specific molecules that facilitate transfection.Polyplexes using 25-kDa polyethylenimine (PEI) and plasmid-encoding green fluorescent protein (GFP) were delivere... |
|
|
Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry to identify contaminants in water: an insight on environmental forensics.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1345 , 86-97, (2014) Ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QqTOF-MS) acquiring full scan MS data for quantification, and automatic data dependent information product ion spectra (IDA-MS/MS) without any predefinition of the io... |
|
|
Risk assessment of pesticides detected in surface water of the Alqueva reservoir (Guadiana basin, southern of Portugal).
Sci. Total Environ. 488-489 , 208-19, (2014) The purpose of this study was to evaluate the potential impact of the pesticides detected in the Alqueva reservoir (Guadiana Basin, South Iberian Peninsula) on the aquatic organisms belonging to this ecosystem. For this purpose, the occurrence and risk assess... |
|
|
Caloric content of Daphnia magna as reflect of propanil stress during a short-term exposure and its relationship to long-term responses.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 35(3) , 465-72, (2013) The present study investigates energy stores changes in the aquatic invertebrate Daphnia magna following a 5-d exposure to propanil. Juveniles of D. magna were exposed to sublethal propanil concentrations (0.07, 0.10, 0.21 and 0.55 mgl(-1)) which were used pr... |
|
|
Integration of biological monitoring, environmental monitoring and computational modelling into the interpretation of pesticide exposure data: introduction to a proposed approach.
Toxicol. Lett. 213(1) , 49-56, (2012) Open field, variability of climatic and working conditions, and the use of complex mixtures of pesticides makes biological and environmental monitoring in agriculture, and therefore risk assessment and management, very complicated. A need of pointing out alte... |
|
|
Characterization of the propanil biodegradation pathway in Sphingomonas sp. Y57 and cloning of the propanil hydrolase gene prpH.
J. Hazard. Mater. 196 , 412-9, (2011) In our previous study, the isoproturon-degrading strain Sphingomonas sp. Y57 was isolated from the wastewater treatment system of an herbicide factory. Interestingly, this strain also showed the ability to degrade propanil (3,4-dichloropropionamilide). The pr... |
|
|
Propionate addition enhances the biodegradation of the xenobiotic herbicide propanil and its metabolite.
Bioresour. Technol. 127 , 195-201, (2013) This study investigated ways of stimulating the biodegradation rates of the commonly applied herbicide, 3,4-dichloropropionanilide (propanil), and its metabolite, 3,4-dichloroaniline (DCA), as well as the growth rate of propanil- and DCA-degrading organisms i... |
|
|
Dissipation of propanil and 3,4 dichloroaniline in three different rice management systems.
J. Environ. Qual. 41(5) , 1487-96, (2012) This study focused on the dissipation of propanil and 3,4 dichloroaniline (3,4 DCA) over time in the soil, field water, inlet water, and outlet water of paddy fields under three management systems: conventional water seeding (CON), conventional water seeding ... |
|
|
Biodegradation of the herbicide propanil, and its 3,4-dichloroaniline by-product in a continuously operated biofilm reactor.
World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29(3) , 467-74, (2013) The persistence of propanil in soil and aquatic environments along with the possible accumulation of toxic degradation products, such as chloroanilines, is of environmental concern. In this work, a continuous small-scale bioprocess to degrade the herbicide pr... |
|
|
Biological treatment of propanil and 3,4-dichloroaniline: kinetic and microbiological characterisation.
Water Res. 44(17) , 4980-91, (2010) Propanil (3,4-dichloropropionanilide) is a widely used herbicide, applied worldwide in rice paddies. Propanil is primarily transformed in nature to 3,4-dichloroaniline (DCA), which is more slowly biodegradable. Both compounds have adverse health and ecotoxici... |