| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
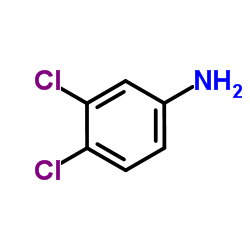 |
3,4-Dichloroaniline
CAS:95-76-1 |
|
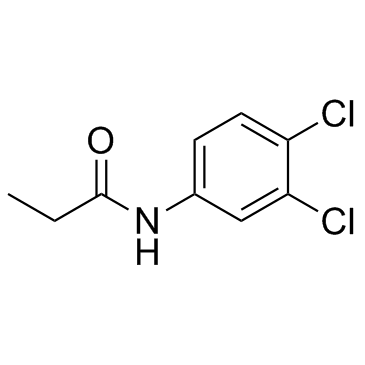 |
Propanil
CAS:709-98-8 |