Dibromobimane
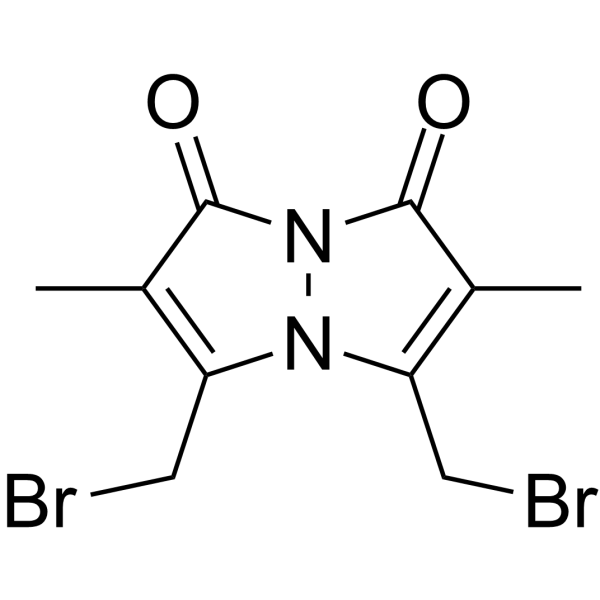
Dibromobimane structure
|
Common Name | Dibromobimane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 68654-25-1 | Molecular Weight | 350.00700 | |
| Density | 1.98g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 371.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H10Br2N2O2 | Melting Point | 170-172ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 178.6ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Thiol labeling with bromobimanes.
Meth. Enzymol. 143 , 76, (1987)
|
|
|
Bromobimanes--fluorescent labeling agents for histochemical detection of sulfur containing neuropeptides in semithin sections.
Histochemistry 86 , 281, (1987) Sulfur containing neuropeptides could be demonstrated in semithin sections of invertebrate nervous tissue, especially of gastropods, by using the bromobimanes as fluorescent labeling agents for thiol groups. Semithin sections showed a brilliant fluorescence o... |
|
|
Physicochemical changes in phosphorylase kinase induced by its cationic activator Mg(2+).
Protein Sci. 22(4) , 444-54, (2013) For over four decades free Mg(2+) ions, that is, those in excess of MgATP, have been reported to affect a wide variety of properties of phosphorylase kinase (PhK), including its affinity for other molecules, proteolysis, chemical crosslinking, phosphorylation... |
|
|
The C-terminus of H-Ras as a target for the covalent binding of reactive compounds modulating Ras-dependent pathways.
PLoS ONE 6(1) , e15866, (2011) Ras proteins are crucial players in differentiation and oncogenesis and constitute important drug targets. The localization and activity of Ras proteins are highly dependent on posttranslational modifications at their C-termini. In addition to an isoprenylate... |
|
|
ArsD residues Cys12, Cys13, and Cys18 form an As(III)-binding site required for arsenic metallochaperone activity.
J. Biol. Chem. 282(23) , 16783-91, (2007) The ArsA ATPase is the catalytic subunit of the ArsAB pump encoded by the arsRDABC operon of Escherichia coli plasmid R773. ArsD is a metallochaperone that delivers As(III) to ArsA, increasing its affinity for As(III), thus conferring resistance to environmen... |
|
|
Modification of the actin interface of skeletal myosin subfragment-1 by treatment with dibromobimane.
Eur. J. Biochem. 159(3) , 555-61, (1986) Recently, by treating the head portion of skeletal myosin subfragment-1 (S1) with the bifunctional agent dibromobimane, we introduced an intramolecular covalent cross-link which resulted in the stabilisation of an internal loop in the heavy chain structure of... |
|
|
Mapping protein interfaces with a fluorogenic cross-linker and mass spectrometry: application to nebulin-calmodulin complexes.
Biochemistry 40(26) , 7903-13, (2001) Nebulin is a giant multifunctional protein that is thought to serve as both a length-regulating protein ruler and calcium/CaM-mediated regulatory protein on the thin filaments of the skeletal muscle sarcomere. To define molecular interfaces between nebulin an... |
|
|
Dibromobimane as a fluorescent crosslinking reagent.
Anal. Biochem. 225(1) , 174-6, (1995)
|
|
|
Conformations of the signal recognition particle protein Ffh from Escherichia coli as determined by FRET.
J. Mol. Biol. 351(2) , 417-30, (2005) The signal recognition particle (SRP) initiates the co-translational targeting of proteins to the plasma membrane in bacteria by binding to the N-terminal signal sequence emerging from the translating ribosome. SRP in Escherichia coli is composed of one prote... |
|
|
Bromobimane crosslinking studies in oligomycin-sensitive ATPase from beef heart mitochondria. Mr 31 000 protein crosslinked.
FEBS Lett. 150(1) , 207-10, (1982) Using a bromobimane fluorescent label the Mr 31 000 protein band oligomycin-sensitive (OS)-ATPase from beef heart mitochondria is shown to become much intensified by 2-mercaptopropionylglycine. In the presence of 3.5 nmol/mg protein of the thiol reagent ATP-P... |