DAUDA
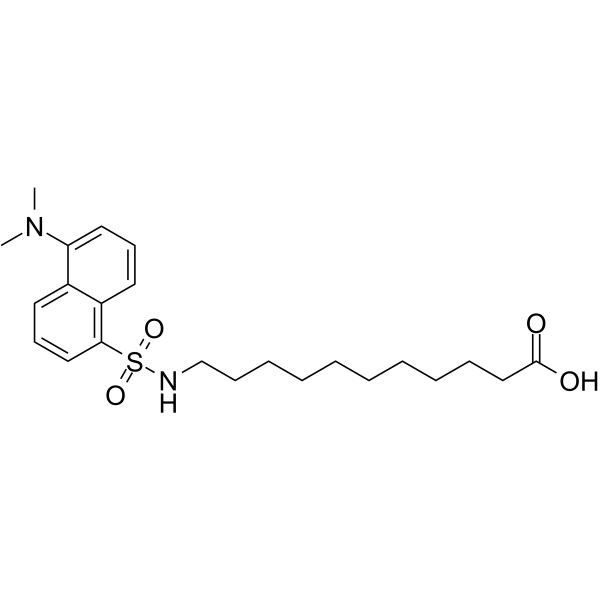
DAUDA structure
|
Common Name | DAUDA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 73025-02-2 | Molecular Weight | 434.592 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 607.9±53.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C23H34N2O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 321.5±30.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Lipid-free antigen B subunits from echinococcus granulosus: oligomerization, ligand binding, and membrane interaction properties.
PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9(3) , e0003552, (2015) The hydatid disease parasite Echinococcus granulosus has a restricted lipid metabolism, and needs to harvest essential lipids from the host. Antigen B (EgAgB), an abundant lipoprotein of the larval stage (hydatid cyst), is thought to be important in lipid sto... |
|
|
Mutations of recombinant rat liver fatty acid-binding protein at residues 102 and 122 alter its structural integrity and affinity for physiological ligands.
Biochem. J. 314 ( Pt 3) , 943-9, (1996) Rat liver fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) is able to accommodate a wide range of non-polar anions in addition to long-chain fatty acids. This property means that the liver protein is functionally different from other FABPs from intestine, muscle and adipose... |
|
|
Binding of recombinant rat liver fatty acid-binding protein to small anionic phospholipid vesicles results in ligand release: a model for interfacial binding and fatty acid targeting.
Biochemistry 38(51) , 16932-40, (1999) A number of intracellular proteins bind to negatively charged phospholipid membranes, and this interfacial binding results in a conformational change that modulates the activity of the protein. Using a fluorescent fatty acid analogue, 11-[5-(dimethylamino)nap... |
|
|
Biochemical characterisation of a hydrophobic ligand binding protein from the tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta.
Int. J. Parasitol. 31(7) , 653-60, (2001) The cestode Hymenolepis diminuta contains an abundant, cytoplasmic, hydrophobic ligand, binding protein (H-HLBP). Studies with polarity sensitive probes suggest a single hydrophobic binding site, the results also indicate that the single tryptophan in the mol... |
|
|
Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein, an MHC class I-related glycoprotein regulator of adipose tissues: modification or abrogation of ligand binding by site-directed mutagenesis.
Biochemistry 45(7) , 2035-41, (2006) Zn-alpha(2)-glycoprotein (ZAG) is a soluble lipid-mobilizing factor associated with cancer cachexia and is a novel adipokine. Its X-ray crystal structure reveals a poly(ethylene glycol) molecule, presumably substituting for a higher affinity natural ligand, o... |
|
|
The binding of natural and fluorescent lysophospholipids to wild-type and mutant rat liver fatty acid-binding protein and albumin.
Biochem. J. 307 ( Pt 1) , 305-11, (1995) Rat liver fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) is able to bind a wide range of non-polar anionic ligands, including lysophospholipids. In order to understand the nature of lysophospholipid interactions with liver FABP, the binding of natural lysophospholipids an... |
|
|
The secretory Onchocerca volvulus protein OvS1/Ov20 exhibits the capacity to compete with serum albumin for the host's long-chain fatty acids.
Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 105(2) , 273-9, (2000) The mechanism by which filarial parasites derive fatty acids bound to the host's carrier protein is poorly understood. The capacity of a secretory protein of Onchocerca volvulus (OvS1/Ov20) to compete with serum albumin for arachidonic and other fatty acids w... |
|
|
Turn scanning by site-directed mutagenesis: application to the protein folding problem using the intestinal fatty acid binding protein.
Protein Sci. 7(8) , 1821-8, (1998) We have systematically mutated residues located in turns between beta-strands of the intestinal fatty acid binding protein (IFABP), and a glycine in a half turn, to valine and have examined the stability, refolding rate constants and ligand dissociation const... |
|
|
A native 13-kDa fatty acid binding protein from the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1674(2) , 200-4, (2004) A 13-kDa fatty acid binding protein (FABP) (Fh13) has been isolated from the cytosol of adult Fasciola hepatica and its physicochemical and binding characteristics determined. Fh13 appears to exist as a dimer in native solution. Binding of the fluorescent fat... |
|
|
A fluorescent fatty acid probe, DAUDA, selectively displaces two myristates bound in human serum albumin.
Protein Sci. 20(12) , 2095-101, (2011) 11-(Dansylamino) undecanoic acid (DAUDA) is a dansyl-type fluorophore and has widely used as a probe to determine the binding site for human serum albumin (HSA). Here, we reported that structure of HSA-Myristate-DAUDA ternary complex and identified clearly th... |