3-Bromopropylamine hydrobromide
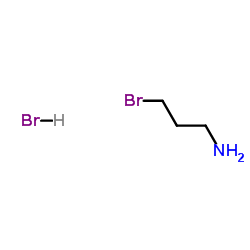
3-Bromopropylamine hydrobromide structure
|
Common Name | 3-Bromopropylamine hydrobromide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5003-71-4 | Molecular Weight | 218.918 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 150.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H9Br2N | Melting Point | 171-172 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 44.9ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Direct Pore Binding as a Mechanism for Isoflurane Inhibition of the Pentameric Ligand-gated Ion Channel ELIC.
Sci. Rep. 5 , 13833, (2015) Pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs) are targets of general anesthetics, but molecular mechanisms underlying anesthetic action remain debatable. We found that ELIC, a pLGIC from Erwinia chrysanthemi, can be functionally inhibited by isoflurane and ot... |
|
|
Inhibition of tissue-bound semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase by two haloamines, 2-bromoethylamine and 3-bromopropylamine.
Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 385(1) , 154-61, (2001) Various mammalian tissues contain membrane-bound amine oxidase termed semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO). A variety of compounds has been identified as relatively selective SSAO inhibitors, but those inhibitors currently available also inhibit monoa... |
|
|
Modification of cysteine.
Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. Chapter 15 , Unit15.1, (2001) This unit describes a number of methods for modifying cysteine residues of proteins and peptides by reduction and alkylation procedures. A general procedure for alkylation of cysteine residues in a protein of known size and composition with haloacyl reagents ... |
|
|
Rational design of ligands targeting triplet repeating transcripts that cause RNA dominant disease: application to myotonic muscular dystrophy type 1 and spinocerebellar ataxia type 3.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(28) , 9767-79, (2009) Herein, we describe the design of high affinity ligands that bind expanded rCUG and rCAG repeat RNAs expressed in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and spinocerebellar ataxia type 3. These ligands also inhibit, with nanomolar IC(50) values, the formation of RNA... |
|
|
Inhibition of copper amine oxidase by haloamines: a killer product mechanism.
Biochemistry 36(9) , 2595-602, (1997) The observation that the alkylamines 2-Br-ethylamine and 2-C1-ethylamine and 1,2-diaminoethane, the shortest diamine, are irreversible inhibitors of several copper amine oxidases led to the investigation of the mechanism by which these compounds react with th... |
|
|
Identification of cysteine residues alkylated with 3-bromopropylamine by protein sequence analysis.
Anal. Biochem. 210(1) , 39-44, (1993) A new reagent for the routine identification of cysteine residues during protein sequencing is described. This method employs 3-bromopropylamine to alkylate cysteines in proteins after reduction with dithiothreitol. Upon sequencing of the protein on an Applie... |
|
|
On-line procedures for alkylation of cysteine residues with 3-bromopropylamine prior to protein sequence analysis.
Anal. Biochem. 221(2) , 374-8, (1994) We have previously shown that 3-bromopropylamine offers several advantages over other alkylating reagents in the modification and subsequent identification of cysteine residues by protein sequencing. We describe here simple on-sequencer procedures for alkylat... |
|
|
Quantitation of cysteine residues alkylated with 3-bromopropylamine by amino acid analysis.
Anal. Biochem. 216(1) , 61-6, (1994) A new versatile reagent, 3-bromopropylamine, for the quantitative analysis of cysteine residues in proteins and peptides is reported. When added to amino acid standards, the 3-bromopropylamine derivative of cysteine, S-3-aminopropylcysteine, elutes in a uniqu... |