fusidic acid
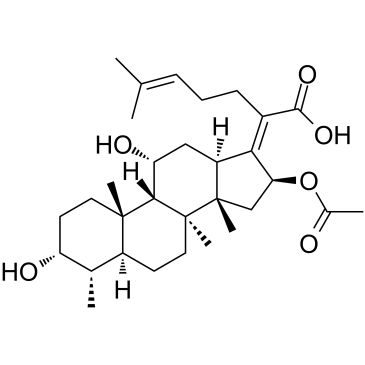
fusidic acid structure
|
Common Name | fusidic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6990-06-3 | Molecular Weight | 516.709 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 635.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C31H48O6 | Melting Point | 190-192ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 197.7±25.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Antibiotic exposure in a low-income country: screening urine samples for presence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in coagulase negative staphylococcal contaminants.
PLoS ONE 9(12) , e113055, (2014) Development of antimicrobial resistance has been assigned to excess and misuse of antimicrobial agents. Staphylococci are part of the normal flora but are also potential pathogens that have become essentially resistant to many known antibiotics. Resistances i... |
|
|
Multiple roles for Enterococcus faecalis glycosyltransferases in biofilm-associated antibiotic resistance, cell envelope integrity, and conjugative transfer.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59 , 4094-105, (2015) The emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria and the limited availability of new antibiotics are of increasing clinical concern. A compounding factor is the ability of microorganisms to form biofilms (communities of cells encased in a protective extracellula... |
|
|
Enterococcus faecalis 6-phosphogluconolactonase is required for both commensal and pathogenic interactions with Manduca sexta.
Infect. Immun. 83(1) , 396-404, (2014) Enterococcus faecalis is a commensal and pathogen of humans and insects. In Manduca sexta, E. faecalis is an infrequent member of the commensal gut community, but its translocation to the hemocoel results in a commensal-to-pathogen switch. To investigate E. f... |
|
|
EbpA vaccine antibodies block binding of Enterococcus faecalis to fibrinogen to prevent catheter-associated bladder infection in mice.
Sci. Transl. Med. 6(254) , 254ra127, (2014) Enterococci bacteria are a frequent cause of catheter-associated urinary tract infections, the most common type of hospital-acquired infection. Treatment has become increasingly challenging because of the emergence of multiantibiotic-resistant enterococcal st... |
|
|
Cellular pharmacokinetics and intracellular activity of the novel peptide deformylase inhibitor GSK1322322 against Staphylococcus aureus laboratory and clinical strains with various resistance phenotypes: studies with human THP-1 monocytes and J774 murine macrophages.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59 , 5747-60, (2015) GSK1322322 is a peptide deformylase inhibitor active against Staphylococcus aureus strains resistant to currently marketed antibiotics. Our aim was to assess the activity of GSK1322322 against intracellular S. aureus using an in vitro pharmacodynamic model an... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo activities of three oxazolidinones against nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(6) , 3217-23, (2014) Oxazolidinones represent a new class of antituberculosis drugs that exert their function by inhibiting protein synthesis. Here, we compared the activities of three oxazolidinones, linezolid, PNU-100480, and AZD5847, against latent tuberculosis using a simple ... |
|
|
A 12-year survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in Greece: ST80-IV epidemic?
Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 20(11) , O796-803, (2014) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an important cause of both healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA) and community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) infections. Severe MRSA infections have been associated with the virulence factor Panton-Valentine le... |
|
|
Characterization of pediatric hospital-associated infection caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in mainland China.
Infect Dis (Lond) 47 , 410-7, (2015) This study was conducted to investigate the clinical features of hospital-associated infections (HAIs) caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Chinese children, and the molecular characteristics of the bacteria.Patients with HAIs cause... |
|
|
Eruption in a patient with Crohn disease.
JAMA Dermatol. 149(1) , 97-102, (2013)
|
|
|
Crystal structures of EF-G-ribosome complexes trapped in intermediate states of translocation.
Science 340(6140) , 1236086, (2013) Translocation of messenger and transfer RNA (mRNA and tRNA) through the ribosome is a crucial step in protein synthesis, whose mechanism is not yet understood. The crystal structures of three Thermus ribosome-tRNA-mRNA-EF-G complexes trapped with β,γ-imidogua... |