| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
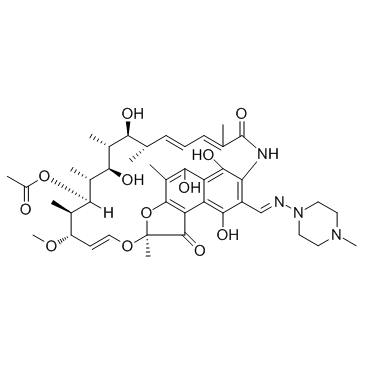 |
Rifampicin
CAS:13292-46-1 |
|
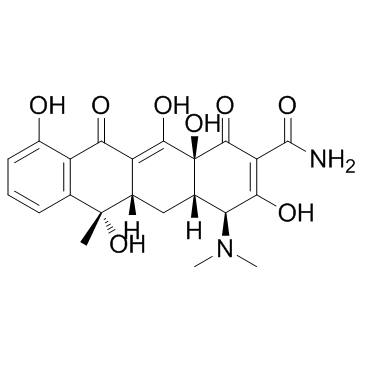 |
Tetracycline
CAS:60-54-8 |
|
 |
Erythromycin
CAS:114-07-8 |
|
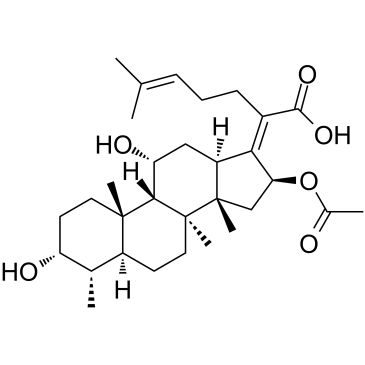 |
fusidic acid
CAS:6990-06-3 |
|
 |
Chloramphenicol
CAS:56-75-7 |
|
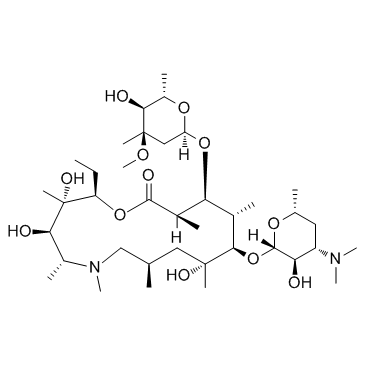 |
Azithromycin
CAS:83905-01-5 |