UBP 302
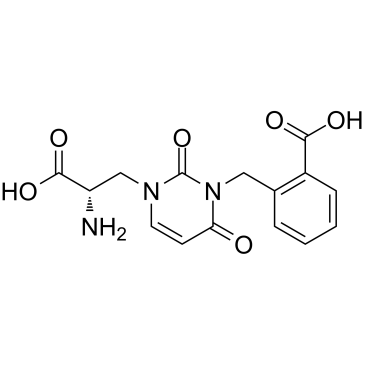
UBP 302 structure
|
Common Name | UBP 302 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 745055-91-8 | Molecular Weight | 333.29600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H15N3O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
The limitations of diazepam as a treatment for nerve agent-induced seizures and neuropathology in rats: comparison with UBP302.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 351(2) , 359-72, (2014) Exposure to nerve agents induces prolonged status epilepticus (SE), causing brain damage or death. Diazepam (DZP) is the current US Food and Drug Administration-approved drug for the cessation of nerve agent-induced SE. Here, we compared the efficacy of DZP w... |
|
|
High-Throughput Screen of GluK1 Receptor Identifies Selective Inhibitors with a Variety of Kinetic Profiles Using Fluorescence and Electrophysiology Assays.
J. Biomol. Screen. 20 , 708-19, (2015) GluK1, a kainate subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors, exhibits an expression pattern in the CNS consistent with involvement in pain processing and migraine. Antagonists of GluK1 have been shown to reduce pain signaling in the spinal cord and trigeminal ... |
|
|
A rat model of nerve agent exposure applicable to the pediatric population: The anticonvulsant efficacies of atropine and GluK1 antagonists.
Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 284 , 204-16, (2015) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) after nerve agent exposure induces status epilepticus (SE), which causes brain damage or death. The development of countermeasures appropriate for the pediatric population requires testing of anticonvulsant treatments... |