Citiolone
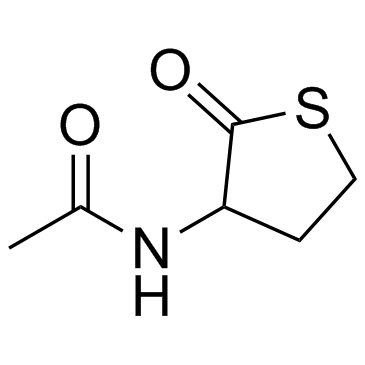
Citiolone structure
|
Common Name | Citiolone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1195-16-0 | Molecular Weight | 159.20600 | |
| Density | 1.263 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 427.265ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9NO2S | Melting Point | 109-111ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 212.202ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
|
Interleukin-1 beta increases the activity of superoxide dismutase in rat pancreatic islets.
Endocrinology 130(5) , 2851-7, (1992) The suppressive effects of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) on the function of pancreatic islets may be related to induction of gene transcription and protein synthesis. Presently, the effects of human recombinant IL-1 beta (rIL-1 beta) on the activities of sup... |
|
|
Inability of thiol compounds to restore CNS arylsulfatases inhibited by methyl mercury.
Pharmacol. Toxicol. 69(1) , 71-4, (1991) Arylsulfatase A and B activities have been analysed in different areas of the CNS (olfactory bulbs, cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, medulla oblongata and spinal cord) during methyl mercuric chloride (MMC), N-acetyl-DL-homocysteine thiolactone (NAHT) and glu... |
|
|
Recurrent fixed drug eruption caused by citiolone.
J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 7(3) , 193-4, (1997) Citiolone (N-acetylhomocysteinethiolactone) is a thiolic-derived medication frequently used in Spain and in other countries as a mucolytic agent for the treatment of certain hepatic disorders. Mucolytic drugs have rarely been implicated in the fixed drug erup... |
|
|
Differential effects of methylmercury, thiols, and vitamins on galactosidases of nervous and non-nervous tissues.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 49(1) , 71-7, (1992)
|
|
|
Fixed drug eruption due to citiolone.
Contact Dermatitis 33(5) , 352, (1995)
|
|
|
Prevention of low dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes by acetyl-homocysteine-thiolactone.
Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 13(1-2) , 95-102, (1991) We used acetyl-homocysteine-thiolactone (citiolone) as an enhancer of superoxide dismutase (SOD), a free radical scavenger, in order to assay any possible prevention of the insulitis and subsequent B cell damage caused by streptozotocin (STZ) when given in mu... |
|
|
Macrophages and antioxidant status in the NOD mouse pancreas.
J. Cell. Biochem. 71(4) , 479-90, (1998) This study showed that citiolone (CIT), a free radical scavenger, significantly increased superoxide dismutase (P < 0.001 vs. untreated NOD, NMMA-treated, and silica-treated animals), catalase (P < 0.01 vs. untreated NOD), and glutathione peroxidase (P < 0.00... |
|
|
Differential therapeutic responses of thiol compounds in the reversal of methylmercury inhibited acid phosphatase and cathepsin E in the central nervous system of rat.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 49(1) , 78-84, (1992)
|
|
|
Comparison of monothiols and vitamin therapy administered alone or in combinations during methylmercury poisoning.
Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 52(2) , 182-9, (1994)
|
|
|
Phosphamidon neurotoxicity: protection by acetylhomocysteine thiolactone.
Neuroreport 2(1) , 61-3, (1991) The present study was undertaken to evaluate the neurotoxic effects of the organophosphate, phosphamidon, on glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity and concentration of sulphhydryl groups, and to study the possible protection against these effects by the si... |