3-(2-Iodoacetamido)-PROXYL
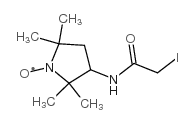
3-(2-Iodoacetamido)-PROXYL structure
|
Common Name | 3-(2-Iodoacetamido)-PROXYL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 27048-01-7 | Molecular Weight | 325.16700 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 415.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18IN2O2 | Melting Point | 162-164ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 205.1ºC | |
|
Characterization of ERM transactivation domain binding to the ACID/PTOV domain of the Mediator subunit MED25.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43 , 7110-21, (2015) The N-terminal acidic transactivation domain (TAD) of ERM/ETV5 (ERM38-68), a PEA3 group member of Ets-related transcription factors, directly interacts with the ACID/PTOV domain of the Mediator complex subunit MED25. Molecular details of this interaction were... |
|
|
Functional role of the flexible N-terminal extension of FKBP38 in catalysis.
Sci. Rep. 3 , 2985, (2013) FKBP38 regulates apoptosis through unique interactions with multiple regulators including Bcl-2. Interestingly, the peptidylprolyl isomerase activity of FKBP38 is only detectable when it binds to calcium-saturated calmodulin (CaM/Ca(2+)). This, in turn, permi... |
|
|
Escherichia coli antitoxin MazE as transcription factor: insights into MazE-DNA binding.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43(2) , 1241-56, (2015) Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules are pairs of genes essential for bacterial regulation upon environmental stresses. The mazEF module encodes the MazF toxin and its cognate MazE antitoxin. The highly dynamic MazE possesses an N-terminal DNA binding domain through ... |
|
|
A fully enzymatic method for site-directed spin labeling of long RNA.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42(15) , e117, (2014) Site-directed spin labeling is emerging as an essential tool to investigate the structural and dynamical features of RNA. We propose here an enzymatic method, which allows the insertion of a paramagnetic center at a specific position in an RNA molecule. The t... |
|
|
Role of the C-terminal domain in the structure and function of tetrameric sodium channels.
Nat. Commun. 4 , 2465, (2013) Voltage-gated sodium channels have essential roles in electrical signalling. Prokaryotic sodium channels are tetramers consisting of transmembrane (TM) voltage-sensing and pore domains, and a cytoplasmic carboxy-terminal domain. Previous crystal structures of... |
|
|
Spin labeled calmodulin: a new probe for studying Ca2+ and macromolecular interactions.
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 356 , 20-32, (1980)
|
|
|
Characterization of long-range structure in the denatured state of staphylococcal nuclease. I. Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement by nitroxide spin labels.
J. Mol. Biol. 268(1) , 158-69, (1997) Structural analysis of delta131delta, a fragment model of the denatured state of staphylococcal nuclease, has been extended by obtaining long-range distance restraints between protein chain segments based on paramagnetic relaxation enhancement methods. PROXYL... |
|
|
Structure and orientation of T4 lysozyme bound to the small heat shock protein alpha-crystallin.
J. Mol. Biol. 375(4) , 1026-39, (2008) We have determined the structural changes that accompany the formation of a stable complex between a destabilized mutant of T4 lysozyme (T4L) and the small heat shock protein alpha-crystallin. Using pairs of fluorescence or spin label probes to fingerprint th... |
|
|
Electron paramagnetic resonance reveals a large-scale conformational change in the cytoplasmic domain of phospholamban upon binding to the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase.
Biochemistry 43(19) , 5842-52, (2004) We used EPR spectroscopy to probe directly the interaction between phospholamban (PLB) and its regulatory target, the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase (SERCA). Synthetic monomeric PLB was prepared with a single cytoplasmic cysteine at residue 11, which was th... |
|
|
Mapping the substrate-binding site of a human class mu glutathione transferase using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Biochemistry 31(11) , 2912-20, (1992) The substrate-binding site of a human muscle class mu glutathione transferase has been characterized using high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Isotopic labeling has been used to simplify one-dimensional proton NMR spectra of the Tyr and H... |