L 701324
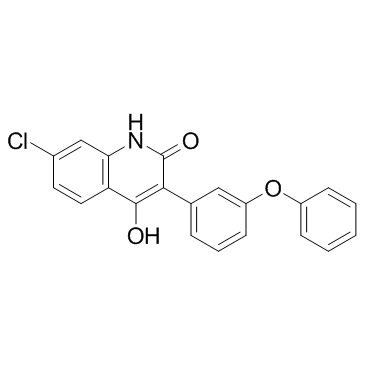
L 701324 structure
|
Common Name | L 701324 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 142326-59-8 | Molecular Weight | 363.794 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 584.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H14ClNO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 307.4±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
NMDA/glutamate mechanism of magnesium-induced anxiolytic-like behavior in mice.
Pharmacol. Rep. 60(5) , 655-63, (2008) The anxiolytic-like activity of magnesium in mice during the elevated plus maze (EPM) has been demonstrated previously. In the present study, we examined the involvement of NMDA/glutamate receptor ligands on the magnesium effect on the EPM. We demonstrated th... |
|
|
NMDA/glutamate mechanism of antidepressant-like action of magnesium in forced swim test in mice.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 88(2) , 158-64, (2007) Antidepressant-like activity of magnesium in forced swim test (FST) was demonstrated previously. Also, enhancement of such activity by joint administration of magnesium and antidepressants was shown. However, the mechanism(s) involved in such activity remain ... |
|
|
Activation of the NMDA/glutamate receptor complex antagonizes the NMDA antagonist-induced antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test.
Pharmacol. Rep. 59(5) , 595-600, (2007) The antidepressant activity of NMDA receptor antagonists has been demonstrated, and their mechanism of action was based on the assumption of their selectivity for the NMDA receptor only. However, no direct evidence for the NMDA receptor role in this activity ... |
|
|
Are glycineB sites involved in the development of morphine tolerance?
Pol. J. Pharmacol. 56(1) , 51-7, (2004) Numerous data have indicated that competitive and non-competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists attenuate the development of tolerance to the analgesic effect of morphine. This study extends these findings on the effects of glycine(B) site ... |
|
|
An examination of NMDA receptor contribution to conditioned responding evoked by the conditional stimulus effects of nicotine.
Psychopharmacology 213 , 131-141, (2011) Research using a drug discriminated goal-tracking (DGT) task showed that the N-methyl-D: -aspartate (NMDA) channel blocker MK-801 (dizocilpine) reduced the nicotine-evoked conditioned response (CR).Given the unknown mechanism of the effect, Experiment 1 repli... |
|
|
Activation of supraspinal NMDA receptors by both D-serine alone or in combination with morphine leads to the potentiation of antinociception in tail-flick test of rats.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 565(1-3) , 89-97, (2007) Although there is a variety of information concerning the effects of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor on opioid-induced antinociception at the spinal level, little is known about the effects at the supraspinal level. To clarify the role of the NMDA re... |
|
|
Cannabinoid-induced increase in relapse-like drinking is prevented by the blockade of the glycine-binding site of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.
Neuroscience 158(2) , 465-73, (2009) The endocannabinoid system is a neuromodulatory system which controls the release of multiple neurotransmitters, including glutamate and both, the endocannabinoid and glutamatergic systems, have been implicated in alcohol relapse. Cannabinoid agonists induce ... |
|
|
Antiallodynic effects of NMDA glycine(B) antagonists in neuropathic pain: possible peripheral mechanisms.
Brain Res. 1048(1-2) , 218-27, (2005) NMDA receptors are implicated in central sensitisation underlying chronic pain, and NMDA antagonists have a potential for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Functional NMDA receptors are also present on primary afferents, where they may play a role in pro-noc... |
|
|
Attenuation of morphine dependence and withdrawal by glycine B site antagonists in rats.
Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 68(1) , 157-61, (2001) Numerous data indicate that noncompetitive and competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists inhibit the development of physical dependence on opioids when these substances are administered together, and NMDA receptor antagonists are used at lo... |
|
|
Lowered brain stimulation reward thresholds in rats treated with a combination of caffeine and N-methyl-D-aspartate but not alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate or metabotropic glutamate receptor-5 receptor antagonists.
Behav. Pharmacol. 17(4) , 295-302, (2006) Previous studies suggested that adenosine A1 and A2A receptor agonists counteract behavioral effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists while adenosine receptor antagonists may produce opposite effects enhancing the actions of NMDA receptor a... |