2-Nitroimidazole
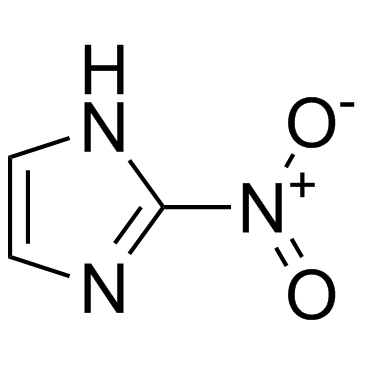
2-Nitroimidazole structure
|
Common Name | 2-Nitroimidazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 527-73-1 | Molecular Weight | 113.075 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 373.6±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H3N3O2 | Melting Point | 287 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 179.7±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
A (99m)Tc-labeled misonidazole analogue: step toward a (99m)Tc-alternative to [18F]fluromisonidazole for detecting tumor hypoxia.
Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 30(2) , 79-86, (2015) The PET radiopharmaceutical [(18)F]Fluromisonidazole ([(18)F]FMISO) is presently the agent of choice for the clinical imaging of tumor hypoxia. Considering the logistic advantages of (99m)Tc and wider availability of SPECT machines, a (99m)Tc-radiopharmaceuti... |
|
|
The synthesis and radiolabeling of 2-nitroimidazole derivatives of cyclam and their preclinical evaluation as positive markers of tumor hypoxia.
J. Nucl. Med. 43(6) , 837-50, (2002) The cyclam ligand (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) was condensed with various azomycin-containing synthons to produce chemical compounds that could chelate radioactive metals. It was expected that these radiolabeled markers would become bound selectively t... |
|
|
The oxygen dependence of the reduction of nitroimidazoles in a radiolytic model system.
Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 10(8) , 1323-6, (1984) Radiation chemical reductions using eaq- and CO2- have been carried out in the presence of oxygen with metronidazole, p-nitroacetophenone, misonidazole and three other 2-nitroimidazoles. Low concentrations of oxygen were found to effectively inhibit the reduc... |
|
|
Imaging hypoxia and angiogenesis in tumors.
Radiol. Clin. North Am. 43(1) , 169-87, (2005) There is a clear need in cancer treatment for a noninvasive imaging assay that evaluates the oxygenation status and heterogeneity of hypoxia and angiogenesis in individual patients. Such an assay could be used to select alternative treatments and to monitor t... |
|
|
A comparison of tumor and normal tissue levels of acidic, basic and neutral 2-nitroimidazole radiosensitizers in mice.
Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 12(7) , 1117-20, (1986) Pharmacokinetic studies were carried out in mice after co-administration of 2-nitroimidazoles with differing prototropic properties: Ro 03-8799, misonidazole, SR 2508, and azomycin. In addition, the distribution of sensitizers in different areas of individual... |
|
|
Radiosensitization by misonidazole, pimonidazole and azomycin and intracellular uptake in human tumour cell lines.
Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 57(2) , 361-72, (1990) The radiosensitization of two human tumour in vitro cell lines, HT-1080 and LoVo, has been compared with that of the Chinese hamster cell line V79-379A. Although the two human tumour cell lines were more radiosensitive than the V79 cell line sensitizer, enhan... |
|
|
Stereospecific deuteration of alpha-furanosyl azomycin nucleosides: a model reaction for tritium radiolabeling.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18(11) , 3256-60, (2008) Stereospecific synthesis of 1-alpha-d-(2-deuteroribofuranosyl)-2-nitroimidazole (2'-[(2)H]-alpha-AZR) is reported. This, deuteration was independent of the configuration of C-2' -OH group (arabinose or ribose) in sugar moiety of starting molecules. Slightly b... |
|
|
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of [(18)F]F-GAZ, a novel oxygen-mimetic azomycin-glucose conjugate, for imaging hypoxic tumor.
Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 27(8) , 473-80, (2012) Several F-18-labeled 2-nitroimidazole (azomycin) derivatives have been proposed for imaging hypoxia using positron emission tomography (PET). Their cell penetration is based on passive diffusion, which limits their intracellular concentration maxima. The purp... |
|
|
Synthesis and hypoxia selective radiosensitization potential of beta-2-FAZA and beta-3-FAZL: fluorinated azomycin beta-nucleosides.
Med. Chem. 5(2) , 118-29, (2009) (18)F-Labelled fluoroazomycin arabinoside ([(18)F]FAZA) is a 2-nitroimidazole (azomycin) based PET tracer used extensively in cancer clinics to diagnose tumour hypoxia. The hypoxia-specific uptake and rapid blood clearance kinetics of FAZA contribute to good ... |
|
|
A dual hypoxic marker technique for measuring oxygenation change within individual tumors.
Br. J. Cancer 78(2) , 163-9, (1998) Rodent tumour models have been the 'workhorse' for tumour oxygenation research and for investigating radiobiological hypoxic fraction. Because of the intertumour heterogeneity of blood flow and related parameters, most studies have pooled information derived ... |