2-Nitroimidazole
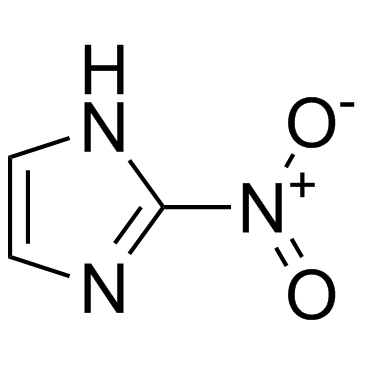
2-Nitroimidazole structure
|
Common Name | 2-Nitroimidazole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 527-73-1 | Molecular Weight | 113.075 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 373.6±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H3N3O2 | Melting Point | 287 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 179.7±23.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2-NitroimidazoleAzomycin is an antibiotic which can be active against aerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. |
| Name | 2-nitroimidazole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Azomycin is an antibiotic which can be active against aerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial[1] |
| In Vitro | Azomycin is an antibiotic which can be active against aerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is found that Azomycin is also active against a variety of anaerobic bacteria[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 373.6±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 287 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H3N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 113.075 |
| Flash Point | 179.7±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 113.022530 |
| PSA | 74.50000 |
| LogP | 0.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.612 |
| InChIKey | YZEUHQHUFTYLPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=[N+]([O-])c1ncc[nH]1 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NI7875000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~66% 
2-Nitroimidazole CAS#:527-73-1 |
| Literature: Yap, Suwan; Woodman, Owen L.; Crack, Peter J.; Williams, Spencer J. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2011 , vol. 21, # 17 p. 5102 - 5106 |
|
~% 
2-Nitroimidazole CAS#:527-73-1 |
| Literature: Luijten, W. C. M. M.; Thuijl, J. van Organic Mass Spectrometry, 1982 , vol. 17, # 7 p. 299 - 303 |
|
~% 
2-Nitroimidazole CAS#:527-73-1 |
| Literature: Davis, Dwight P.; Kirk, Kenneth L.; Cohen, Louis A. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1982 , vol. 19, p. 253 - 256 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933290090. other compounds containing an unfused imidazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
A (99m)Tc-labeled misonidazole analogue: step toward a (99m)Tc-alternative to [18F]fluromisonidazole for detecting tumor hypoxia.
Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 30(2) , 79-86, (2015) The PET radiopharmaceutical [(18)F]Fluromisonidazole ([(18)F]FMISO) is presently the agent of choice for the clinical imaging of tumor hypoxia. Considering the logistic advantages of (99m)Tc and wider... |
|
|
The synthesis and radiolabeling of 2-nitroimidazole derivatives of cyclam and their preclinical evaluation as positive markers of tumor hypoxia.
J. Nucl. Med. 43(6) , 837-50, (2002) The cyclam ligand (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) was condensed with various azomycin-containing synthons to produce chemical compounds that could chelate radioactive metals. It was expected that ... |
|
|
The oxygen dependence of the reduction of nitroimidazoles in a radiolytic model system.
Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 10(8) , 1323-6, (1984) Radiation chemical reductions using eaq- and CO2- have been carried out in the presence of oxygen with metronidazole, p-nitroacetophenone, misonidazole and three other 2-nitroimidazoles. Low concentra... |
| 2-Nitroimidazol |
| Azomycin |
| 2-Nitro-1H-imidazole |
| MFCD00005185 |
| 2-Nitroimidazole |
| EINECS 208-425-5 |
| 1H-Imidazole, 2-nitro- |
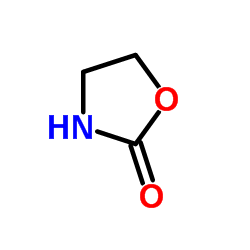 CAS#:497-25-6
CAS#:497-25-6 CAS#:3964-18-9
CAS#:3964-18-9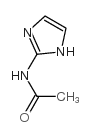 CAS#:52737-49-2
CAS#:52737-49-2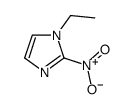 CAS#:10045-33-7
CAS#:10045-33-7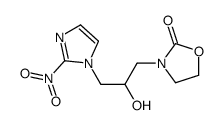 CAS#:129449-06-5
CAS#:129449-06-5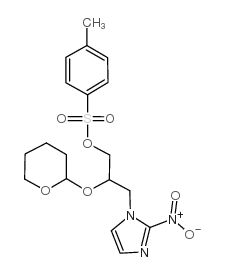 CAS#:150196-34-2
CAS#:150196-34-2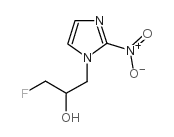 CAS#:13551-89-8
CAS#:13551-89-8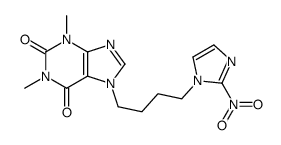 CAS#:137046-51-6
CAS#:137046-51-6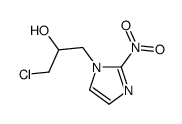 CAS#:13551-86-5
CAS#:13551-86-5 CAS#:1671-82-5
CAS#:1671-82-5
