Methacholine (chloride)
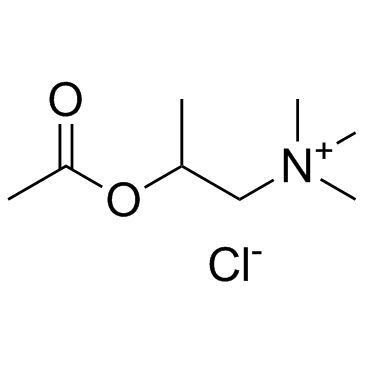
Methacholine (chloride) structure
|
Common Name | Methacholine (chloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 62-51-1 | Molecular Weight | 195.687 | |
| Density | 1.1028 (rough estimate) | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H18ClNO2 | Melting Point | 171-173ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state of neural stem cells.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007) The identification of self-renewing and multipotent neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain holds promise for the treatment of neurological diseases and has yielded new insight into brain cancer. However, the complete repertoire of signaling pathways ... |
|
|
Hyaluronan mediates airway hyperresponsiveness in oxidative lung injury.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 308 , L891-903, (2015) Chlorine (Cl2) inhalation induces severe oxidative lung injury and airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) that lead to asthmalike symptoms. When inhaled, Cl2 reacts with epithelial lining fluid, forming by-products that damage hyaluronan, a constituent of the extra... |
|
|
MAG-EPA and 17,18-EpETE target cytoplasmic signalling pathways to reduce short-term airway hyperresponsiveness.
Pflugers Arch. 467 , 1591-605, (2015) This study was aimed to investigate the role of eicosapentaenoic acid monoacylglyceride (MAG-EPA) and 17,18-epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (17,18-EpETE) on the regulation of contractile reactivity and nuclear protein expression in 72-h-cultured and TNF-α-treated ... |
|
|
Vitamin D supplementation blocks pulmonary structural and functional changes in a rat model of perinatal vitamin D deficiency.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 307(11) , L859-67, (2014) Whereas epidemiological data strongly link vitamin D (VD) deficiency to childhood asthma, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unknown. Although VD is known to stimulate alveolar epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, promoting perinatal lung maturation, ... |
|
|
Alveolar macrophages are critical for the inhibition of allergic asthma by mesenchymal stromal cells.
J. Immunol. 191(12) , 5914-24, (2013) Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) possess reparative and immunoregulatory properties, making them attractive candidates for cellular therapy. However, the majority of MSCs administered i.v. encounter a pulmonary impasse and soon disappear from the ... |
|
|
The modulation of large airway smooth muscle phenotype and effects of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in the repeatedly allergen-challenged rat.
Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 304(12) , L853-62, (2013) Allergen challenges induce airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and increased airway smooth muscle (ASM) mass in the sensitized rat. Whether the remodeled ASM changes its phenotype is uncertain. We examined, in sensitized Brown Norway rats, the effects of multipl... |
|
|
ORMDL3 transgenic mice have increased airway remodeling and airway responsiveness characteristic of asthma.
J. Immunol. 192(8) , 3475-87, (2014) Orosomucoid-like (ORMDL)3 has been strongly linked with asthma in genetic association studies. Because allergen challenge induces lung ORMDL3 expression in wild-type mice, we have generated human ORMDL3 zona pellucida 3 Cre (hORMDL3(zp3-Cre)) mice that overex... |
|
|
Effect of carvacrol on tracheal responsiveness, inflammatory mediators, total and differential WBC count in blood of sensitized guinea pigs.
Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood.) 238(2) , 200-8, (2013) The effects of carvacrol on tracheal responsiveness (TR) to methacholine and ovalbumin (OA), serum nitric oxide (NO) concentration, total and differential white blood cells (WBC) in blood of sensitized guinea pigs were examined. Five groups of guinea pigs sen... |
|
|
Increased ornithine-derived polyamines cause airway hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of asthma.
Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 48(6) , 694-702, (2013) Up-regulation of arginase contributes to airways hyperresponsiveness (AHR) in asthma by reducing L-arginine bioavailability for the nitric oxide (NO) synthase isozymes. The product of arginase activity, L-ornithine, can be metabolized into polyamines by ornit... |
|
|
Insulin resistance in the vasculature.
J. Clin. Invest. 123(3) , 1003-4, (2013) Insulin resistance is typically defined as a reduced ability of insulin to induce glucose uptake by target tissues such as fat and skeletal muscle cells. It accompanies several disease states, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, hepatitis C, and polycystic ov... |