TDCPP
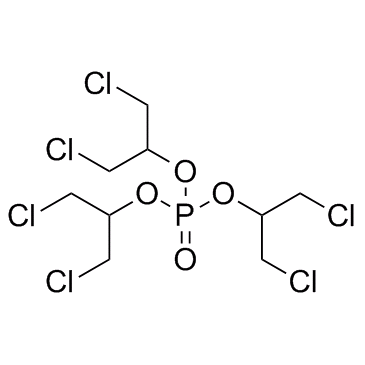
TDCPP structure
|
Common Name | TDCPP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13674-87-8 | Molecular Weight | 430.905 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 457.4±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H15Cl6O4P | Melting Point | -64°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 377.7±35.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
|
Haloalkylphosphorus hydrolases purified from Sphingomonas sp. strain TDK1 and Sphingobium sp. strain TCM1.
Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80(18) , 5866-73, (2014) Phosphotriesterases catalyze the first step of organophosphorus triester degradation. The bacterial phosphotriesterases purified and characterized to date hydrolyze mainly aryl dialkyl phosphates, such as parathion, paraoxon, and chlorpyrifos. In this study, ... |
|
|
Developmental exposure to the organophosphorus flame retardant tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate: estrogenic activity, endocrine disruption and reproductive effects on zebrafish.
Aquat. Toxicol. 160 , 163-71, (2015) Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP) is an organophosphate flame retardant that is detectable in the environment and biota, prompting concern over its risk to wildlife and human health. Our objective was to investigate whether long-term exposure to l... |
|
|
Urinary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants: temporal variability and correlations with house dust concentrations.
Environ. Health Perspect. 121 , 580-5, (2013) A reduction in the use of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) because of human health concerns may result in an increased use of and human exposure to organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs). Human exposure and health studies of OPFRs are lacking.We sough... |
|
|
Early zebrafish embryogenesis is susceptible to developmental TDCPP exposure.
Environ. Health Perspect. 120 , 1585-91, (2012) Chlorinated phosphate esters (CPEs) are widely used as additive flame retardants for low-density polyurethane foams and have frequently been detected at elevated concentrations within indoor environmental media.To begin characterizing the potential toxicity o... |
|
|
Identification of flame retardants in polyurethane foam collected from baby products.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 45 , 5323-31, (2011) With the phase-out of PentaBDE in 2004, alternative flame retardants are being used in polyurethane foam to meet flammability standards. However, insufficient information is available on the identity of the flame retardants currently in use. Baby products con... |
|
|
Novel and high volume use flame retardants in US couches reflective of the 2005 PentaBDE phase out.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 46 , 13432-9, (2012) California's furniture flammability standard Technical Bulletin 117 (TB 117) is believed to be a major driver of chemical flame retardant (FR) use in residential furniture in the United States. With the phase-out of the polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) FR... |
|
|
Organophosphorus flame retardants and phthalate esters in indoor dust from different microenvironments: Bioaccessibility and risk assessment.
Chemosphere 150 , 528-35, (2016) Incidental ingestion of indoor dust is an important pathway for human exposure to organophosphorus flame retardants (OPFRs) and phthalate esters (PAEs). However, little is known about their bioaccessibility in indoor dust. In this study, indoor dust samples w... |
|
|
Toxicity of TDCPP and TCEP on PC12 cell: Changes in CAMKII, GAP43, tubulin and NF-H gene and protein levels
Toxicol. Lett. 227(3) , 164-71, (2014) • The toxicity of TDCPP/TCEP in undifferentiated and differentiated PC12 cells was modelled. • Both cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity were elicited by TDCPP/TCEP. • CAMKII, GAP43, tubulin and NF-H maybe useful biomarkers for the cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity. |