H-Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-OH
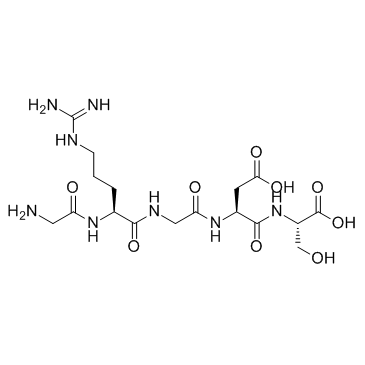
H-Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96426-21-0 | Molecular Weight | 490.46800 | |
| Density | 1.66 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H30N8O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
|
Substantial Differentiation of Human Neural Stem Cells Into Motor Neurons on a Biomimetic Polyurea.
Macromol. Biosci. 15 , 1206-11, (2015) To find the first restorative treatment for spinal cord injury (SCI), researchers have focused on stem cell therapies. However, one obstacle is the lack of an implantable cell scaffold that can support efficient motor neuron (MN) differentiation and prolifera... |
|
|
The phosphatidylserine receptor TIM4 utilizes integrins as coreceptors to effect phagocytosis.
Mol. Biol. Cell 25(9) , 1511-22, (2014) T-cell immunoglobulin mucin protein 4 (TIM4), a phosphatidylserine (PtdSer)-binding receptor, mediates the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. How TIM4 exerts its function is unclear, and conflicting data have emerged. To define the mode of action of TIM4, we us... |
|
|
Aerosol-stable peptide-coated liposome nanoparticles: a proof-of-concept study with opioid fentanyl in enhancing analgesic effects and reducing plasma drug exposure.
J. Pharm. Sci. 103(8) , 2231-9, (2014) Previously, we reported a novel pressurized olfactory drug (POD) delivery device that deposits aerosolized drug preferentially to upper nasal cavity. This POD device provided sustained central nervous system (CNS) levels of soluble morphine analgesic effects.... |
|
|
Latency associated peptide has in vitro and in vivo immune effects independent of TGF-beta1.
PLoS Biol. 3 , e1914, (2008) Latency Associated Peptide (LAP) binds TGF-beta1, forming a latent complex. Currently, LAP is presumed to function only as a sequestering agent for active TGF-beta1. Previous work shows that LAP can induce epithelial cell migration, but effects on leukocytes ... |
|
|
In vitro evaluation of an RGD-functionalized chitosan derivative for enhanced cell adhesion.
Carbohydr. Polym. 90(4) , 1494-500, (2012) Tissue repair is a spontaneous process that is initiated on wounding. However, if this complex mechanism is impaired or not sufficient the use of biomaterials might increase the chance of successful healing. In this view, an RGD-functionalized polymer was dev... |
|
|
PCL-PEG-based nanoparticles grafted with GRGDS peptide: preparation and surface analysis by XPS.
Biomacromolecules 8(12) , 3977-83, (2007)
|
|
|
Addition of biological functionality to poly(epsilon-caprolactone) films.
Biomacromolecules 8(8) , 2416-21, (2007) Biodegradable polyesters such as poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) have a number of biomedical applications; however, their usage is often limited by a lack of biological functionality. In this paper, a PCL-based polymer containing pendent groups activated by ... |
|
|
[Effects of bioactive modification of poly-D,L-lactide acid scaffolds on the biological behaviors of the seed cells].
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 31(2) , 289-94, (2011) To study the changes in the biological behavior of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) transfected with red fluorescent protein by lentivirus (RFP-BMSCs) seeded on in poly-D, L-lactide acid (PDLLA) scaffolds with bioactive modification by ammonia plasm... |
|
|
Rapid cellular internalization of multifunctional star polymers prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization.
Biomacromolecules 11(9) , 2199-203, (2010) Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) star polymers containing GRGDS (Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser) peptide sequences on the star periphery were synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (PEGMA), GRGDS modified... |
|
|
Integrin stimulation favors uptake of macromolecules by cardiomyocytes in vitro.
Cell Physiol. Biochem. 26 , 999-1010, (2010) Previously, our research group showed that integrin stimulation induces release of cardiac troponin I from viable neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes (NRCMs), but would it also stimulate uptake of exogenous macromolecules? For this purpose, beating NRCMs ... |