| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
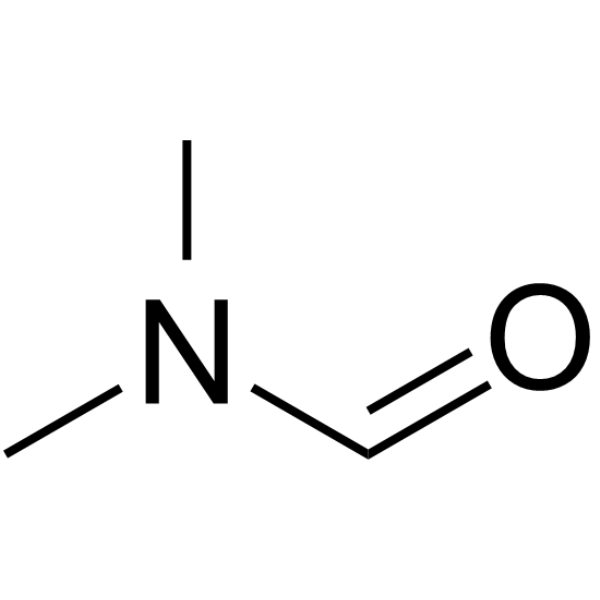 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
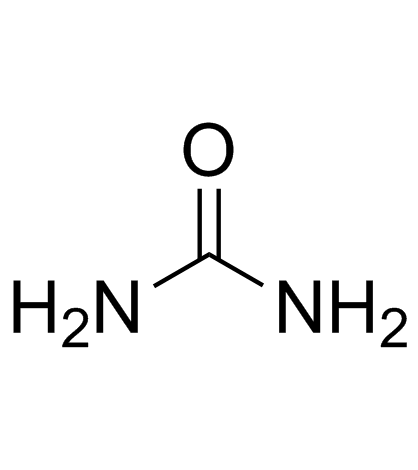 |
Urea
CAS:57-13-6 |
|
 |
Retinoic acid
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
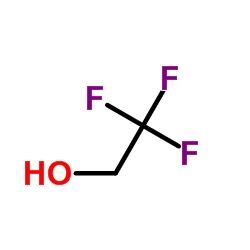 |
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol
CAS:75-89-8 |
|
 |
N-Boc-serinol
CAS:125414-41-7 |
|
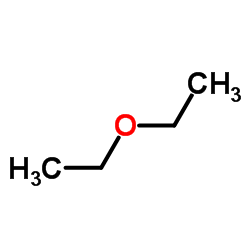 |
Diethyl ether
CAS:60-29-7 |